UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, DC 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2021
or
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from ___________ to ___________
Commission File No. 001-40388
ANEBULO PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 85-1170950 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| 1415 Ranch Road 620 South, Suite 201 Lakeway, Texas |
78734 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
(512) 598-0931
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered | ||
| Common Stock | ANEB | Nasdaq Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☒ | Smaller reporting company | ☒ | |
| Emerging growth company | ☒ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
As of December 31, 2020, the last day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, there was no public market for the registrant’s common stock. The registrant’s common stock began trading on The Nasdaq Capital Market (“Nasdaq”) on May 7, 2021. The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was $16,382,340 based on the closing price of the registrant’s common stock on Nasdaq on September 15, 2021. In determining the market value of non-affiliate common stock, share of the registrant’s common stock beneficially owned by officers, directors and affiliates have been excluded. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
The number of shares of the registrant’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share, outstanding as of September 15, 2021 was 23,344,567 shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s definitive proxy statement that will be filed for the 2021 annual meeting of stockholders (the “2021 Proxy Statement”) are incorporated by reference in Part III. The 2021 Proxy Statement will be filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year to which this report relates.
Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Table of Contents
In this report, unless otherwise stated or as the context otherwise requires, references to “Anebulo Pharmaceuticals,” “Anebulo,” “Company,” “we,” “us,” “our” and similar references refer to Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The Anebulo logo, and other trademarks or service marks of Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc. appearing in this report are the property of Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc. This report also contains registered marks, trademarks and trade names of other companies. All other trademarks, registered marks and trade names appearing in this report are the property of their respective holders. We do not intend our use or display of other companies’ trade names, trademarks or service marks to imply a relationship with, or endorsement or sponsorship of us by, these other companies.
| 2 |
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This report contains forward-looking statements about us and our industry that involve substantial risks and uncertainties. All statements other than statements of historical facts contained in this report, including statements regarding our future financial condition, business strategy and plans, and objectives of management for future operations, are forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “believe,” “may,” “could,” “will,” “estimate,” “continue,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “seek,” “plan,” “expect,” “should,” “would,” “potentially” or the negative of these terms or similar expressions in this report.
We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and financial trends that we believe may affect our financial condition, results of operations, business strategy and financial needs. These forward-looking statements include the following:
| ● | We have not generated any revenue since our inception and expect to incur future losses and may never become profitable. | |
| ● | We currently rely on a license from a third party, and in the future may rely on additional licenses from other third parties, in relation to our development of ANEB-001, and if we fail to comply with our obligations under our current or future intellectual property license agreements or otherwise experience disruptions to our business relationships with our current or any future licensors, we could lose intellectual property rights that are important to our business. | |
| ● | We currently have no product revenue and will need to raise additional capital, which may be unavailable to us or may cause dilution or place significant restrictions on our ability to operate. | |
| ● | We have less than one year of operating history as a publicly-traded company, and our inexperience could materially and adversely affect us and our stockholders. | |
| ● | If we are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection for important aspects of ANEB-001, or if the scope of the patent protection obtained is not sufficiently broad, our competitors could develop and commercialize products that are similar or identical to ours, and our ability to successfully commercialize our current or future product candidates may be adversely affected. | |
| ● | We may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights throughout the world, which could negatively impact our business. | |
| ● | The expiration or loss of patent protection may adversely affect our future revenues and operating earnings. | |
| ● | Delays in the completion of, or the termination of, a clinical trial for ANEB-001, our lead drug candidate, could adversely affect our business. | |
| ● | If we are not able to obtain any required regulatory approvals for ANEB-001, we will not be able to commercialize our lead drug candidate and our ability to generate revenue will be limited. | |
| ● | Even if we receive regulatory approval for ANEB-001, our lead drug candidate, we may not be able to successfully commercialize the product and the revenue that we generate from its sales, if any, may be limited. | |
| ● | Even if we obtain marketing approval for ANEB-001, we will be subject to ongoing obligations and continued regulatory review, which may result in significant additional expenses. Additionally, ANEB-001 could be subject to labeling and other restrictions and withdrawal from the market and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or if we experience unanticipated problems with ANEB-001. | |
| ● | ANEB-001, our lead drug candidate, may face competition sooner than expected. | |
| ● | We will be completely dependent on third parties to manufacture ANEB-001, and our commercialization of ANEB-001 could be halted, delayed or made less profitable if those third parties fail to obtain manufacturing approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) or comparable foreign regulatory authorities, fail to provide us with sufficient quantities of ANEB-001 or fail to do so at acceptable quality levels or prices. | |
| ● | Any termination or suspension of, or delays in the commencement or completion of, any necessary studies of ANEB-001, our lead drug candidate, for any indications could result in increased costs to us, delay or limit our ability to generate revenue and adversely affect our commercial prospects. | |
| ● | Clinical drug development involves a lengthy and expensive process with an uncertain outcome, and results of earlier studies and trials may not be predictive of future trial results. | |
| ● | Legislative or regulatory reform of the healthcare system may affect our ability to sell our products profitably. | |
| ● | Clinical trials for ANEB-001 have and may in the future be conducted outside the United States and not under an Investigational New Drug Application (“IND”), and where this is the case, the FDA may not accept data from such trials. | |
| ● | Laws impacting the U.S. healthcare system are subject to a great deal of uncertainty, which may result in adverse consequences to our business. |
You should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. Unless required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements to reflect new information or future events or developments. Thus, you should not assume that our silence over time means that actual events are bearing out as expressed or implied in such forward-looking statements. We qualify all of the forward-looking statements in this report by these cautionary statements.
| 3 |
SUMMARY OF MATERIAL RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH OUR BUSINESS
Our business is subject to numerous risks and uncertainties that you should be aware, including those described in the section entitled “Risk Factors.” These risks include the following:
| ● | Our business could be adversely affected by the effects of health epidemics, including the recent COVID-19 pandemic, in regions where third parties for which we rely, as in contract research organizations (“CROs”) or contract manufacturing organizations (“CMOs”), have significant research, development or manufacturing facilities, concentrations of clinical trial sites or other business operations, causing disruption in supplies and services. | |
| ● | We are a clinical-stage biotechnology company and we have incurred net losses since our inception. We anticipate that we will continue to incur significant losses in the future, and may never achieve or maintain profitability. | |
| ● | Our business is highly dependent on our lead product candidate, ANEB-001, and we must complete clinical testing before we can seek regulatory approval and begin commercialization of any of our product candidates. | |
| ● | We depend substantially on intellectual property licensed from third parties, including Vernalis Development Limited, formerly Vernalis (R&D) Limited (“Vernalis”) and termination of any of these licenses could result in the loss of significant rights, which would harm our business. | |
| ● | If we are unable to obtain and maintain sufficient intellectual property protection for our product candidates or if the scope of the intellectual property protection is not sufficiently broad, our ability to commercialize our product candidates successfully and to compete effectively may be adversely affected. | |
| ● | We will need substantial additional funding, and if we are unable to raise capital when needed, we could be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate our product discovery and development programs or commercialization efforts. | |
| ● | We have a limited operating history, which may make it difficult to evaluate the success of our business to date and to assess our future viability. | |
| ● | We are early in our development efforts and have only one product candidate in clinical development. If we are unable to successfully develop and commercialize our product candidate or experience significant delays in doing so, our business may be materially harmed. | |
| ● | Clinical drug development involves a lengthy and expensive process with an uncertain outcome, and the inability to successfully and timely conduct clinical trials and obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates would substantially harm our business. | |
| ● | The results of clinical trials are not necessarily predictive of future results. Our existing product candidate in clinical trials, and any other product candidate we advance into clinical trials, may not have favorable results in later clinical trials or receive regulatory approval. | |
| ● | Our product candidates, the methods used to deliver them or their dosage levels may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties that could delay or prevent their regulatory approval, limit the commercial profile of an approved label or result in significant negative consequences following any regulatory approval. | |
| ● | We face substantial competition, which may result in others discovering, developing or commercializing products before or more successfully than we do. | |
| ● | We and our third-party partners are subject to a multitude of manufacturing risks, any of which could substantially increase our costs and limit supply of our product candidates. | |
| ● | We intend to develop an efficient and highly productive manufacturing supply chain for our drug therapies. Delays in process performance qualification to validate the drug product manufacturing process could delay regulatory approvals, and our development plans and thereby limit our ability to generate revenues. | |
| ● | We are highly dependent on our key personnel and anticipate hiring new key personnel. If we are not successful in attracting and retaining highly qualified personnel, we may not be able to successfully implement our business strategy. |
The summary risk factors described above should be read together with the text of the full risk factors below, in the section entitled “Risk Factors” and the other information set forth in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including our financial statements and the related notes, as well as in other documents that we file with the SEC. The risks summarized above or described in full below are not the only risks that we face. Additional risks and uncertainties not precisely known to us, or that we currently deem to be immaterial may also materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth prospects.
| 4 |
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biotechnology company developing novel solutions for people suffering from acute cannabinoid intoxication (“ACI”) and substance addiction. Our lead product candidate, ANEB-001, is intended to reverse the negative effects of ACI within 1 hour of administration. The signs and symptoms of ACI range from profound sedation to anxiety and panic to psychosis with hallucinations. There is no approved medical treatment currently available to specifically alleviate the symptoms of ACI and we are not aware of any competing products that are further along in the development process than ANEB-001 in reversing the effects of tetrahydrocannabinol (“THC”), the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis. Clinical trials completed to date have shown that ANEB-001 is rapidly absorbed, well tolerated and leads to weight loss, an effect that is consistent with central CB1 antagonism. In March 2021, our European clinical trial applications (which is equivalent to an investigational new drug application in the United States) was accepted in the Netherlands to allow us to utilize ANEB-001 in a Phase 2 proof-of-concept trial for ACI planned for the fourth quarter of 2021.
ACI has become a widespread health issue in the United States, particularly in the increasing number of states that have legalized cannabis for personal and recreational use. The ingestion of large quantities of THC is a major cause of ACI. Excessive ingestion of THC via edible products such as candies and brownies, and intoxication from synthetic cannabinoids (also known as “synthetics,” “K2” or “spice”), are two leading causes of THC-related emergency room visits. Synthetic cannabinoids are analogous to fentanyl for opioids insofar as they are more potent at the cannabinoid receptor than their natural product congener THC.
In recent years, hospital emergency rooms across the United States have seen a dramatic increase in patient visits with cannabis-related conditions. Before the legalization of cannabis, an estimated 450,000 patients visited hospital emergency rooms annually for cannabis-related conditions. In 2014, this number more than doubled to an estimated 1.1 million patients, according to data published in “Trends and Related Factors of Cannabis-Associated Emergency Department Visits in the United States: 2006-2014,” Journal of Addiction Medicine (May/June 2019), which provided a national estimate analyzing data from The Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (“NEDS”), the largest database of U.S. hospital-owned emergency department visits. Based on our own analysis of the most recent NEDS data, we believe that the number of hospitalizations grew to 1.74 million patients in 2018 and was growing at an approximately 15% compounded annual growth rate between 2012 and 2018. We believe the number of cannabis-related hospitalizations and other health problems associated with ACI such as depression, anxiety and mental disorders will continue to increase substantially as more states pass laws legalizing cannabis for medical and recreational use. Given the consequences, there is an urgent need for a treatment to rapidly reverse the symptoms of ACI.
Our Lead Product Candidate
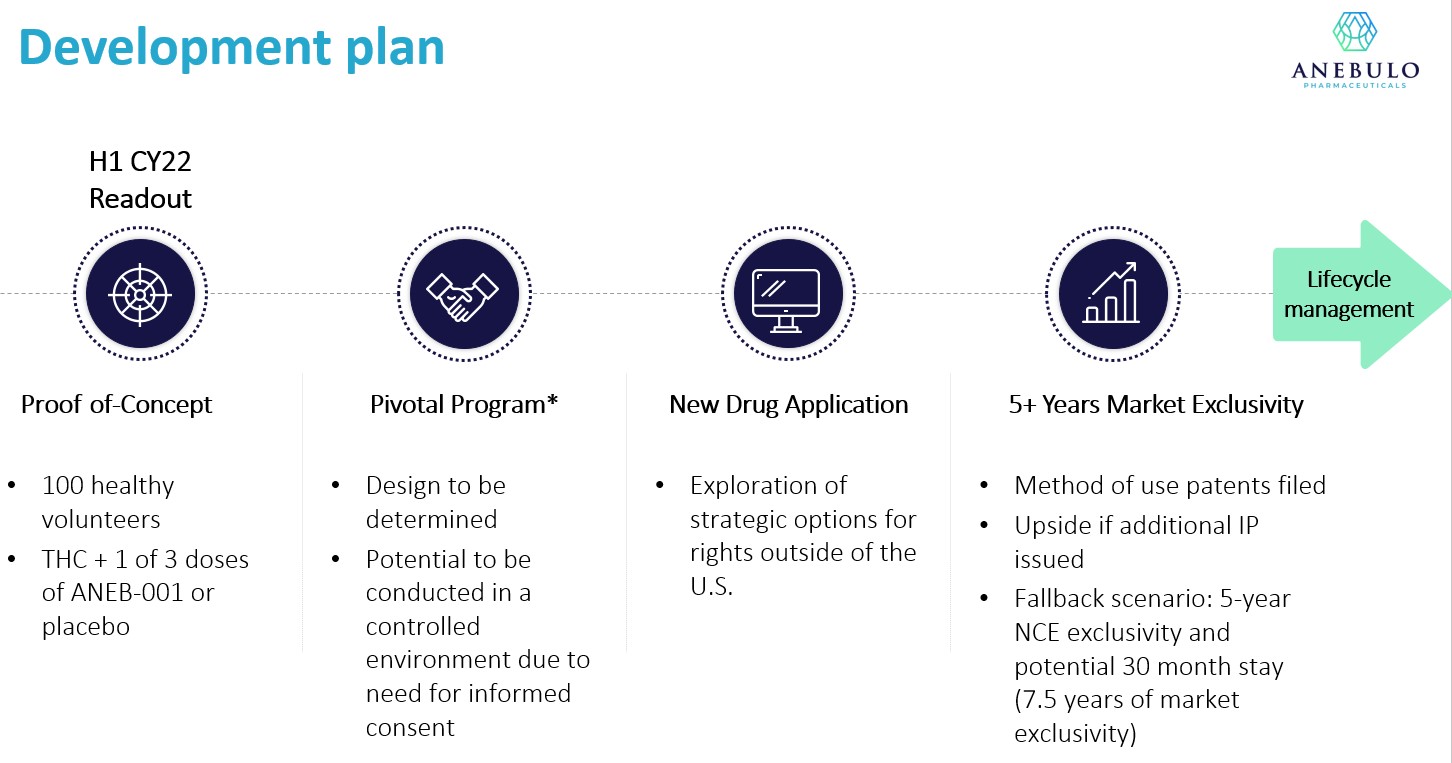
Our objective is to develop and commercialize new treatments options for patients suffering from addiction. Our lead product candidate is ANEB-001, a potent, small molecule cannabinoid receptor antagonist, to address the unmet medical need for a specific antidote for ACI. ANEB-001 is an orally bioavailable, rapidly absorbed treatment that we anticipate will reverse the symptoms of ACI, in most cases within 1 hour of administration. Our proprietary position in the treatment of ACI is protected by rights to two patent applications covering various methods of use of the compound and delivery systems. We anticipate starting our first Phase 2 trial for ANEB-001 in the fourth calendar quarter of 2021.
Cannabinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are naturally occurring and are primarily found in cannabis plant extracts. The two major cannabinoids found in cannabis plant extracts include THC and cannabidiol (“CBD”). These compounds bind themselves to CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, which are found throughout the body. Specifically, CB1 receptors are concentrated in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are found mostly in peripheral organs and are associated with the immune system. When the chemical compounds bind themselves to these cannabinoid receptors, the process elicits certain physiological responses. Physiological responses to cannabinoids may vary among individuals. Some of the effects of cannabinoids have been shown to impact nervous system functions, immune responses, muscular motor functions, gastrointestinal maintenance, blood sugar management, and the integrity of ocular functions.
| 5 |
Individuals can use or consume cannabinoids in natural or unnatural formulations, orally or by inhalation, and intentionally and unintentionally, all of which can result in intoxication. Natural formulations include edibles and marijuana cigarettes; unnatural formulations include synthetics. Individuals consume cannabinoids orally by ingesting edibles or synthetics and by inhalation through smoking marijuana cigarettes or synthetics. Cannabinoids can also be ingested unintentionally through these same methods where, for example, children consume edibles by mistaking them for common consumer items like candy that would not otherwise contain THC. Symptoms of ACI produced by edibles and synthetics can include psychosis, panic and anxiety, feelings of paranoia, agitation, hallucinations, nausea, vomiting, cardiac arrhythmias, seizures and death. Many of these symptoms can require emergency medical attention and can take hours to days to resolve depending on the particular product and amount ingested. Currently, there is no specific treatment to reverse ACI and physicians have to rely on supportive care, including benzodiazepines, and wait for the body to metabolize the THC or synthetic cannabinoid.

| * | We are relying on studies performed by a third party for a different indication, obesity, and the FDA or a foreign equivalent regulator may disagree with our ability to reference the clinical data generated by such third-party trials in connection with the indication for ACI and addiction. See “Risk Factors – We are relying on clinical trials performed by our licensor Vernalis.” |
Our Market Opportunity
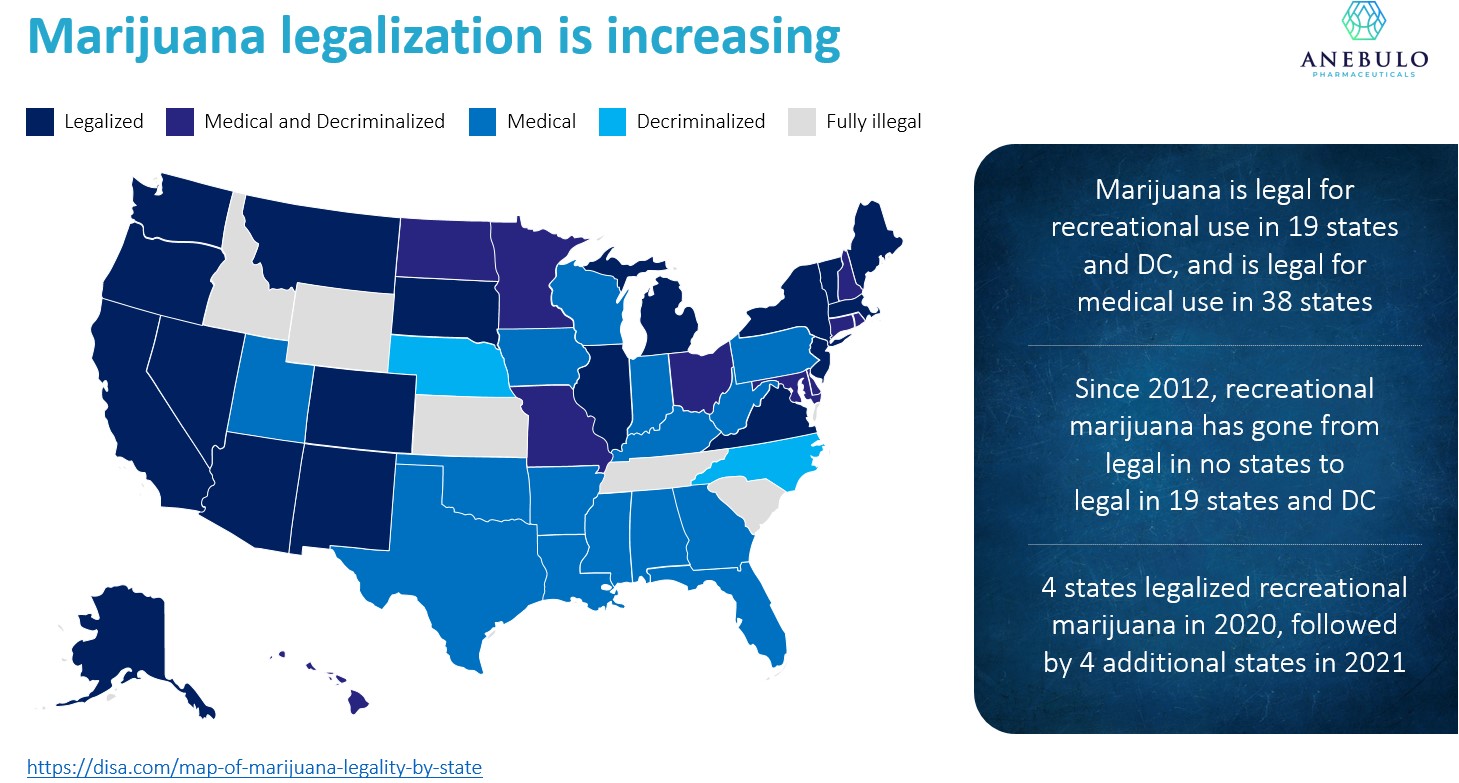
ACI has become a widespread health issue in the United States as an increasing number of states have legalized cannabis for personal and recreational use. As of June 30, 2021, cannabis was legal for recreational use in 19 states and the District of Columbia and legal for medical use in 38 states. Additionally, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and recent news reports have described how the stress, anxiety and depression from the prolonged stay-at-home conditions surrounding the Covid-19 pandemic appears to result in excessive drug and cannabis use by individuals, whether in jurisdictions where such use is legal or not.
| 6 |
ACI frequently occurs due to the ingestion of edibles, which can contain relatively large amounts of THC, and consumption of synthetics. Symptoms of ACI produced by edibles and synthetics can include psychosis, panic and anxiety, feelings of paranoia, agitation, hallucinations, nausea, vomiting, cardiac arrhythmias, seizures and death. These symptoms can require emergency medical attention and can take hours to days to resolve. According to an article published in the Journal of Addiction Medicine that analyzed data from NEDS, an estimated 1.1 million emergency department visits were associated with cannabis in 2014. We have performed our own independent analysis of all currently available NEDS datasets and estimated that the number of cannabis-associated emergency department visits increased to 1.74 million patients in 2018. The number of cannabis-associated emergency department visits has grown at a 15% compounded annual growth rate from 2012 to 2018, which is when states first began legalizing recreational cannabis use.
| 7 |
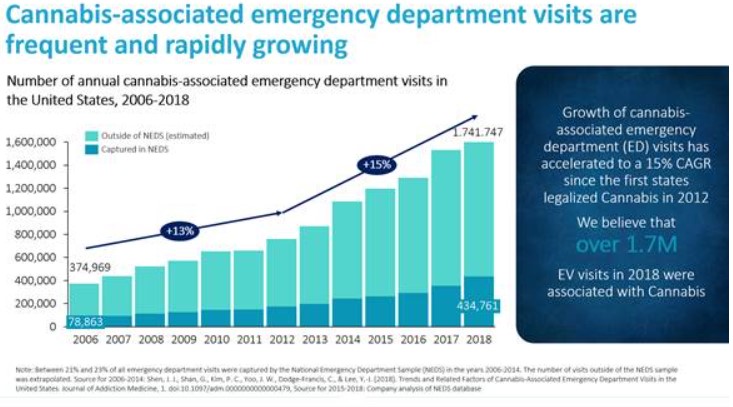
Source for 2006-2014: Shen, J. J., Shan, G., Kim, P. C., Yoo, J. W., Dodge-Francis, C., & Lee, Y.-J. (2018). Trends and Related Factors of Cannabis-Associated Emergency Department Visits in the United States. Journal of Addiction Medicine, 1. doi:10.1097/adm.0000000000000479, Source for 2015-2018: Company analysis of NEDS database.
We believe that both the number of cannabis-associated emergency department visits and the unmet medical need will continue to grow due to the increasing availability and consumption of edibles. In THC-containing edibles, the median dose of THC can be many times more potent than the recommended safe dosage and as much as eight times more potent than a rolled marijuana cigarette. Edibles are frequently manufactured as common consumer products, such as brownies, cookies, candies and gummy snacks with brightly-colored packaging. THC concentrations in edibles peak after a delay of about two to four hours from ingestion. This contrasts with smoking cannabis, which causes THC concentrations to peak in about three to 10 minutes from inhalation. Consumers possibly will approach edibles with the same serving size expectations as consumer products without THC. Moreover, children are particularly at risk for accidentally consuming edibles due to their brightly-colored packaging and formulation into candies and sweets. The confluence of these factors can be dangerous and increases the risk of ACI. Emergency department visits were 33 times more likely for edibles as compared with other routes of cannabis consumption, according to the recent article “Mental Health-related Emergency Department Visits Associated with Cannabis in Colorado,” published in Academic Emergency Medicine (May 2018). Sales of edibles are rapidly growing, according to data collected by Statista, and are expected to continue growing into the future.
In November 2020, we sponsored a survey of U.S. physicians concerning patient emergency room visits for ACI within the past 12 months. Based on a survey of 27 emergency room physicians throughout the United States, the surveyed physicians saw on average 10.5 patients (a range of two to 45 patients) with cannabis intoxication per month. The survey asked these physicians to rank on a scale of 1 to 10 (i) the need for a cannabinoid antagonist to treat cannabis intoxication; (ii) the likelihood of their prescribing a cannabinoid antagonist that reverses cannabis intoxication within 30 minutes of administration; and (iii) the likelihood of such cannabinoid antagonist reducing the need for supportive medication to manage certain cannabis intoxication symptoms, such as agitation and acute psychosis. In response to these questions, the surveyed physicians ranked the need for a cannabinoid antagonist at an average of 7.52 out of 10, the likelihood of prescribing a cannabinoid antagonist that reverses cannabis intoxication within 30 minutes of administration at an average of 7.44 out of 10, and the likelihood of a specific cannabinoid antagonist reducing the need for supportive medication to manage certain ACI symptoms at an average of 7.48 out of 10.
| 8 |
We believe that the market opportunity for our lead product candidate, ANEB-001, will continue to expand and accelerate if additional states pass laws to legalize recreational cannabis use. In Colorado, one of the first states to legalize recreational marijuana, the Colorado Department of Health and Environment reported that by 2018 marijuana use by adults one or more times during the past 30 days roughly doubled in the years following the state’s legalization of cannabis. In July 2021, several U.S. Senators presented a draft bill in the Senate to decriminalize marijuana at the federal level by removing cannabis from the list of controlled substances under the Controlled Substances Act. A separate bill was reintroduced in May 2021 in the U.S. House of Representatives, also seeking to federally legalize marijuana. Although it is currently uncertain whether these bills will be reconciled, passed and signed into law by the President, in the event the use of cannabis is legalized in the United States at the federal level, we believe that the greater anticipated number of users will significantly increase the potential need for our lead candidate.
We believe that overdose due to synthetic cannabinoids is an area with particularly high unmet medical need. Synthetics are among the fastest growing class of psychoactive drugs worldwide and can be as much as 85 times as potent as THC. Unlike edibles and other cannabis products, synthetics have low shipping weights and can more readily evade traditional drug screening methods. This likely reflects the structural promiscuity of the CB1 receptor. In addition, the negative effects of an overdose from synthetics can be longer lasting and more severe when compared with THC. These negative effects could include seizures, and even death.
Our Growth Strategy
Our goal is to create a therapeutic to treat the symptoms of ACI and substance addiction. As noted above, there are currently no FDA approved medical treatments on the market to specifically alleviate the negative psychological effects of ACI. The absence and growing unmet need for such a treatment gives us the unique opportunity to create a novel solution and become a leader in the cannabinoid treatment space. To achieve our goal, our strategy will be guided by the following principles:
| ● | Develop and commercialize our ANEB-001 antagonist in the United States. We anticipate commencing our Phase 2 proof-of-concept study in the fourth calendar quarter of 2021. We believe the data from this study may facilitate discussions of a regulatory path for ANEB-001 in the United States. | |
| ● | Explore strategic collaborations to commercialize ANEB-001. Our plan is to widely commercialize ANEB-001. To accomplish this objective, we may partner with companies that possess a direct sales force and sales representatives. | |
| ● | Strive for capital efficiency in developing ANEB-001. We aim to be capital efficient in our development of ANEB-001 by outsourcing our clinical research and data management. We anticipate this will lower our clinical development costs and improve our ability to efficiently commercialize ANEB-001 if it is approved by the FDA. | |
| ● | Introduce promising product candidate extensions. We are in the initial stages of introducing a non-oral formulation of ANEB-001 with the same API that we intend to develop for use in cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (“CHS”), which is a condition that can develop following long-term use of marijuana and is characterized by cyclical episodes of nausea and vomiting that are not usually responsive to standard care. We believe that antagonizing the paradox emetogenic action of THC at the receptor and helping patients abstain from THC represent the most promising and causal treatment for CHS. | |
| ● | Develop future product candidates to treat substance-related addiction. We intend to leverage our expertise in the endocannabinoid system to develop additional product candidates for the treatment of substance addiction. CB1 antagonists have been shown to be promising in treating substance-related addiction. We believe that there is a large and growing unmet medical need for new treatment options because of the opioid and methamphetamine epidemic. |
| 9 |
Our Clinical Trials and Milestones
We are developing ANEB-001 to quickly and effectively combat the symptoms of ACI.
Preclinical Data
The preclinical characterization of ANEB-001 was performed at Vernalis’ internal laboratory in the United Kingdom between 2003 and 2006. The compound was tested as a displacer in established radioligand binding assays for the CB1 receptor. ANEB-001 displaced the antagonist radioligand, [3H]-SR141716A from the human CB1 receptor with high affinity (0.55 nM) and was shown to be a competitive antagonist in cAMP assays. In vitro testing as a displacer in 90 binding assays and 19 enzyme and functional assays, showed that ANEB-001 had >1000x selectivity with the human CB1 receptor over all other tested receptors. Further, Vernalis demonstrated that oral administration of ANEB-001 reduced hypolocomotion in mice after 30 minutes, effectively reversing the action of THC. C57 mice administered THC 3 mg/kg in 10 minutes pre-test exhibited reduced locomotor activity when placed in automated locomotor activity cages for 15 minutes. Providing it orally at a dose of 30 mg/kg 30 minutes pre-test significantly revered the action of THC on the total activity time parameter (p<0.01 by one way ANOVA and Newman Keuls test, n=7 per group).
In 2006 and 2007, two Phase 1 studies for the treatment of obesity were conducted by Vernalis for ANEB-001.
Phase 1 First Trial
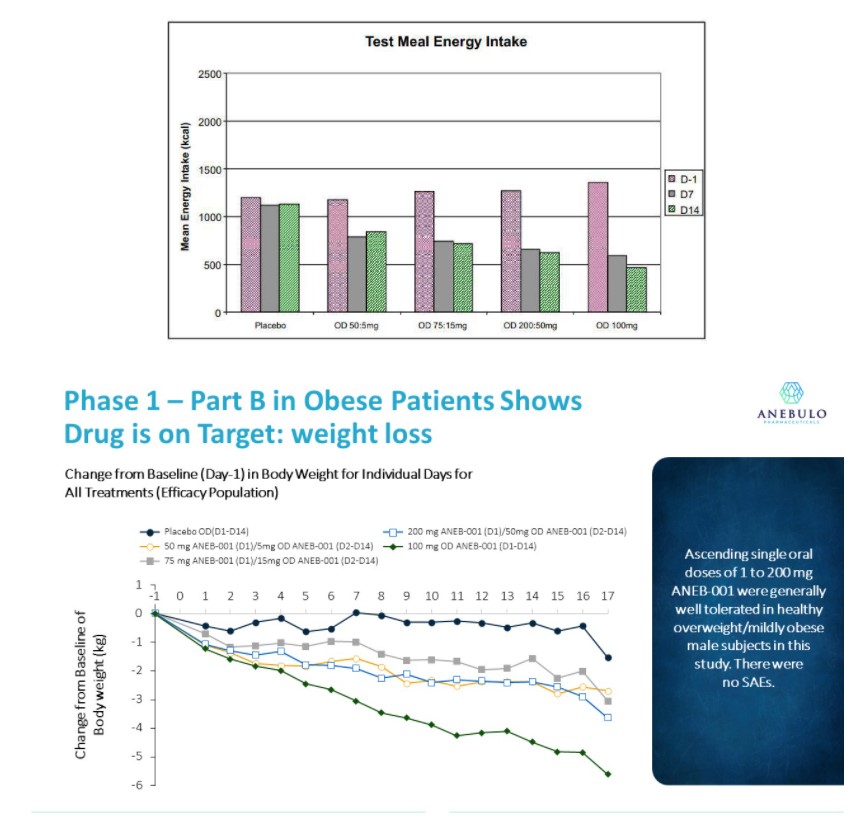
The Phase 1 study (V24343-1Ob-01) administered single (Part A) and multiple (Part B) ascending doses of ANEB-001 for up to 14 days in otherwise healthy overweight and mildly obese subjects.
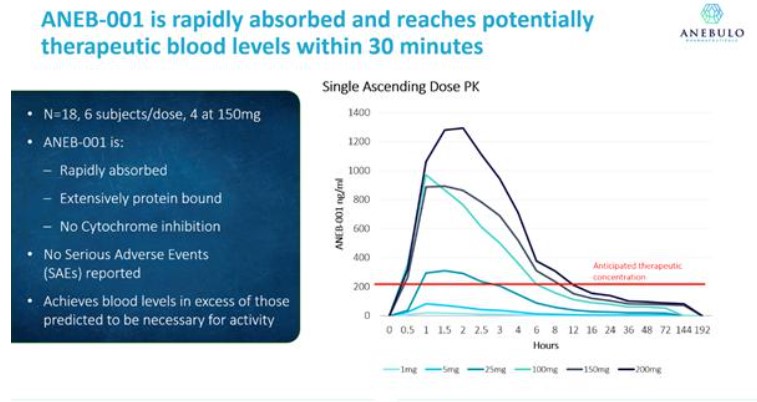
| ● | Part A randomized 18 healthy volunteers to receive either a placebo (n=18) or two single oral doses of ANEB-001, with doses ranging from 1 mg to 200 mg. No severe adverse events were observed in either group in Part A. There was no difference between treatment groups in Part A in overall incidence, number of or severity of adverse events. Probable drug-related events in the treatment arm were nausea (22%), dizziness (11%), hiccups (8%), and decreased appetite (8%). | |
| ● | Part B randomized 32 obese volunteers to receive either a placebo (eight obese volunteers) or four different doses of ANEB-001 for 14 days (24 obese volunteers). No severe adverse events were observed in either group in Part B, but an increased number of mild and moderate adverse events was observed in the obese volunteers who received the two higher dose arms (200/50 mg and 100 mg). The observed adverse events included nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, hiccups, decreased appetite, hyperhidrosis and feeling hot. We believe these adverse events are “on-target,” meaning they reflect CB1 antagonism, because these adverse events have also been observed with other CB1 antagonists. |
Pharmacokinetic measurements in Part A of the Phase 1 study demonstrated that ANEB-001 was rapidly absorbed by the body following oral administration and achieved blood concentrations anticipated to exceed those necessary to block the cannabinoid receptor (as indicated by the red line in the diagram below).
| 10 |
Vernalis also measured the impact of ANEB-001 on anxiety and depression in Part B of the Phase 1 study. Vernalis measured anxiety by using the Spielberger state score, a commonly used measure of trait and state anxiety. Vernalis found no significant impact on anxiety, except for the 200/50 mg arm, which showed increased anxiety at all assessment times. The change was driven by a single subject and may be explained by somatic adverse events, which contributed to the Spielberger score. For depression, HAMD21 was used and small increases were noted in the 75/15 mg and 200/50 mg dose, which we believe were likely driven by somatic symptoms.
Summarizing the results from the Phase 1 study, ANEB-001 doses between 1 mg and 150 mg were found to be very well tolerated in both single and multiple doses with an adverse events profile similar to placebo. There was no observed effect on the cardiovascular system, ECGs, labs or physical exams and no significant effects on anxiety or depression scores.
With regard to pharmacodynamics, a marked reduction in test meal energy intake was seen even at the lowest dose level in Phase 1 Part B (p<0.01 on Day 14 for OD 100 mg, p<0.05 on Day 7 for OD 100 mg, not statistically significant for all other cohorts). Further, Vernalis observed statistically significant decreases in body weight (p<0.001 on Day 14 for OD 100 mg, p<0.05 for OD 50/5 mg and OD 200/50 mg, not significant for OD75/15 mg) indicating that ANEB-001 was able to cross the blood-brain barrier and antagonize central cannabinoid receptors. P-value is the probability that the difference between two data sets was due to chance. The smaller the p-value, the more likely the differences are not due to chance alone. In general, if the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05, the outcome is considered statistically significant. The FDA’s evidentiary standard of efficacy generally relies on a p-value of less than or equal to 0.05.
| 11 |
Phase 1 Second Trial
The second Phase 1 study (V24343-1Ob-02) compared the pharmacokinetics of a single oral dose (1 to 200 mg) of ANEB-001 to eight subjects in fed and fasted states, and to eight subjects that were lean and overweight. There were no apparent differences in the tolerability of ANEB-001 between the subjects that were in fed and fasted states or subjects that were lean and overweight. Total AUC (or area under the curve) was approximately 30% higher in subjects in the fed state compared to the subjects in the fasted state, with similar systemic exposure for the lean and overweight subjects.
| 12 |
The results of the Phase 1 studies demonstrate that ANEB-001 was well tolerated among healthy and obese subjects. There were no serious adverse events. The most commonly reported adverse event was gastrointestinal discomfort, which also occurred in subjects that were administered placebos. Based on the promising results of the Phase 1 studies, we believe ANEB-001 may offer the following clinical and product benefits:
| ● | Oral bioavailability. ANEB-001 will be available as an oral treatment in the form of a pill, capsule or tablet. | |
| ● | Rapid absorption. We believe ANEB-001 can rapidly reverse the signs and symptoms of ACI in as little as 1 hour. | |
| ● | Low likelihood of drug-to-drug interactions. Preclinical testing demonstrated that ANEB-001 did not inhibit the metabolic enzymes cytochromes 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6 and 3A4 at pharmacologically relevant concentrations. | |
| ● | Better treatment option. As an orally administered treatment tested to work in as little as 1 hour, ANEB-001 has the potential to be faster acting than intravenous (“IV”) treatments that may be developed by competitors. In spite of the efforts of competitors listed below (see “Competition” section), we are currently not aware of any competing products that are further along in the development process than ANEB-001 to specifically reverse the symptoms of ACI. | |
| ● | No serious adverse events. A single dose of the drug is unlikely to produce adverse events associated with chronic dosing. The most commonly reported adverse effect in our Phase 1 study was gastrointestinal discomfort, which also occurred in subjects who were administered a placebo. |
We plan to commence a Phase 2 proof-of-concept study in the fourth calendar quarter of 2021 at a center in the Netherlands to test the efficacy of a single dose of ANEB-001 on a population of approximately 100 human subjects who have been administered 10 milligrams of THC that will then be randomized to receive a placebo, low dose, medium dose or high dose of ANEB-001. We anticipate completing the Phase 2 study within approximately six months after commencing the study and having data potentially available in the first half of 2022. We believe this study will lay the foundation for us to engage with the FDA and/or comparable foreign regulatory authorities, file IND with the FDA in the United States and conduct more extensive clinical trials with the goal of generating additional clinical data that will ultimately enable us to file a marketing application with the FDA.
We have engaged CROs to assist us with conducting clinical trials and to provide us with consulting and development services in the various phases of the drug development process. We currently have a consultancy agreement with Traxeus Pharma Services Limited (“Traxeus”), which we entered into on July 15, 2020 (the “Consultancy Agreement”). Pursuant to the Consultancy Agreement, Traxeus provides certain pharmaceutical development services and deliverables to us in relation to the retest of an existing batch of drug substance. These services include the manufacturing and testing of a demonstration batch of the drug substance and the completion of formulation and process development for the drug product. Under the Consultancy Agreement, Traxeus is permitted to provide services to third parties that are not directly competitive to us and we are permitted to engage other CROs. The Consultancy Agreement can be terminated immediately by either party if a material breach is committed and not remedied within 60 days or a party is unable to carry on business, becomes insolvent or is subject to similar processes in any jurisdiction. In addition, we may terminate any statement of work arising under the Consultancy Agreement by providing Traxeus at least 30 days’ written notice. We plan to continue to engage CROs like Traxeus and other pharmaceutical services providers to assist us with clinical trials, the development of our lead product candidate ANEB-001.
Vernalis License Agreement
On May 26, 2020, we entered into an exclusive license agreement (the “License Agreement”) with Vernalis. Pursuant to the License Agreement, Vernalis granted us an exclusive worldwide royalty-bearing license to develop and commercialize a compound that we refer to as ANEB-001, as well as access to and a right of reference with respect to any regulatory materials under its control. The License Agreement allows us to sublicense the rights thereunder to any person with similar or greater financial resources and expertise without Vernalis’ prior consent, provided the proposed sublicensee is not developing or commercializing a product that contains a CB1 antagonist or is for the same indication covered by the trials or market authorization for ANEB-001. In exchange for the exclusive license, we agreed to pay Vernalis a non-refundable signature fee of $150,000, total potential developmental milestone payments of up to $29,900,000, total potential sales milestone payments of up to $35,000,000, and low to mid-single digit royalties on net sales.
| 13 |
Under the License Agreement, we purchased the API for ANEB-001 from Vernalis on an “as is” basis for $20,000. We have the sole discretion to carry out the development and commercialization of ANEB-001, including obtaining regulatory approvals, and we are responsible for all costs and expenses in connection therewith. We have access to certain regulatory materials, including study reports from clinical and non-clinical trials, under Vernalis’ control. We agreed to use commercially reasonable efforts to (i) develop and commercialize ANEB-001 in the United States and certain European countries and (ii) conduct a Phase 2 and human clinical trial within specified periods, which periods could be extended for a nominal fee. We also agreed to provide Vernalis with periodic reports of our activities and notice of market authorization within specified timeframes.
With respect to intellectual property, both parties agreed to retain sole ownership over their respective intellectual property as of the date of the License Agreement. In addition, we retain the sole right over certain patent rights (including patent applications) and know-how controlled by us that are necessary or reasonably useful to developing and commercializing ANEB-001 during the term of the License Agreement.
The License Agreement continues for an indefinite term unless and until it is terminated or until such time as all royalties and other sums cease to be payable thereunder. Our obligations to pay royalties commence upon the first commercial sale of our product and cease upon the later to occur of: (i) the tenth anniversary of the first commercial sale of our product, or (ii) the expiration date of the regulatory exclusivity of our product. We may terminate the License Agreement in its entirety at any time by providing 60 days’ prior notice to Vernalis. Moreover, a party may terminate the License Agreement for cause (i) upon written notice when the other party commits a material breach not remedied within the specified timeframes and defaults on its obligations thereunder, or (ii) when the other party is insolvent as more particularly described therein. In the event of termination, all rights and licenses granted by Vernalis will revert immediately to Vernalis; all outstanding sums as of the termination date will be immediately due and payable to Vernalis; and we will return or destroy, at Vernalis’ request, any regulatory materials, information pertaining to ANEB-001, and any unused API purchased from Vernalis. If Vernalis terminates the License Agreement due to our material breach or insolvency, or if we terminate the License Agreement at will, both parties will negotiate in good faith to grant Vernalis a license to such intellectual property and regulatory materials needed to develop and commercialize ANEB-001 and provide appropriate compensation to us within six months of the termination date.
Competition
The clinical biotechnology industry is a competitive industry characterized by technological innovation and growth. Our competitors include other biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, and public and private research institutions. These entities engage in efforts to research, discover and develop new medicines and treatments for substance use. These entities also seek patent protection and licensing revenues for their research results and may compete with us in recruiting skilled talent. Some of these entities are larger and better funded than us. Our management can make no assurances that we can effectively compete with these competitors. Potential current competitors include Opiant Pharmaceuticals, Inc., which is developing a drinabant injection to treat ACI, and Aelis Farma, which is developing a medication based on a pregnanolone derivative to treat cannabis use disorders.
Research and Development
We are making, and expect to continue to make, substantial expenditures to fund proprietary research and development of our ANEB-001 product candidate and to support preclinical testing and clinical trials necessary for regulatory filings. Our research and development team, including a third-party contract research organization, is continually undertaking efforts to advance research and development goals. During the year ended June 30, 2021 and the period from April 23, 2020 (date of inception) to June 30, 2020, we incurred research and development expenses of approximately $2,270,000 and $150,000, respectively.
| 14 |
Regulation
Government Regulation and Product Approval
We operate in an extensively regulated industry. Governmental authorities at all levels in the United States and in other countries regulate aspects of bringing therapeutics, drugs, and other biologics to market, including research, testing, safety, product approval, development, manufacture, efficacy, quality control, packaging, storage, record-keeping, promotion, labeling, advertising, marketing, distribution, sales, imports and exports of our products.
Under the Controlled Substances Act (the “CSA”), cannabis is currently considered a Schedule I controlled substance and is, therefore, illegal under federal law. A Schedule I controlled substance is defined as a drug or substance that has a high potential for abuse, has no currently accepted medical use in the United States, and lacks accepted safety for use under medical supervision. Although an increasing number of states have legalized cannabis under state laws, the use, possession and cultivation of cannabis remains a violation under federal law. The United States Supreme Court has upheld the federal government’s right to regulate and criminalize cannabis, even for medicinal uses. Federal law criminalizing the use of cannabis preempts contrary or conflicting state laws. As a result, if the federal government enforces the CSA in states that have legalized cannabis for medicinal and/or recreational uses, individuals charged with distributing, possessing with intent to distribute or cultivating cannabis could be subject to fines and/or terms of imprisonment. The maximum penalty is life imprisonment and a $50 million fine.
As a therapeutic product for human use, ANEB-001 will be subject to regulation in the United States by the FDA under the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act (“FDCA”) and similar regulatory requirements in other countries. Regulatory requirements include, among other things, rigorous preclinical and clinical testing. The processes for commercializing our product, obtaining regulatory approval and maintaining compliance with applicable statutes and regulations require the substantial expenditure of time and financial resources and play a significant role in our research and development, production, and marketing activities. Failure to comply with these regulatory processes and other requirements could delay our ability to receive regulatory approvals, adversely affect the commercialization of our product, and hinder our ability to receive royalties or revenues.
In the United States, the FDA regulates drugs under the FDCA and its implementing regulations. Failure to comply with such regulations during and after the product development and approval process could result in administrative or judicial sanctions. Such sanctions include the FDA’s refusal to approve pending applications, withdrawal of an approval, placement a clinical hold, untitled or warning letters, product recalls, seizure of products, partial or complete suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, refusal of government contracts, restitution, disgorgement, civil penalties and criminal penalties. The FDA generally requires the following before a drug can be marketed in the United States:
| ● | Completion of preclinical laboratory tests, animal studies and formulation studies according to Good Laboratory Practices regulations; | |
| ● | Submission of an IND, which must become effective before the commencement of human clinical studies; | |
| ● | Approval by an independent internal review board (“IRB”), at each clinical site before the initiation of each trial; | |
| ● | Performance of adequate and well-controlled human clinical studies according to Good Clinical Practice (“GCP”) regulations, to establish the safety and efficacy of the proposed drug for its intended use; | |
| ● | Preparation and submission of a New Drug Application (“NDA”); | |
| ● | Satisfactory completion of an FDA inspection of the manufacturing facility or facilities where the product, or its components, are produced to ensure compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practice (“CGMP”) regulations and to ensure that the facilities, methods, and controls are adequate to preserve the drug’s identity, strength, quality, and purity; and | |
| ● | FDA review and approval of the NDA. |
| 15 |
Given that the testing and approval process requires a substantial commitment of time, effort and financial resources, we cannot ensure that our product will be granted approval on a timely basis.
As part of the IND, an IND sponsor must submit the preclinical test results, along with manufacturing information, analytical data and any available clinical data or literature, to the FDA. The sponsor must also include a protocol detailing the objectives of the initial clinical study, the parameters for monitoring safety, and the effectiveness criteria to be assessed (among other things) if the initial clinical study lends itself to an efficacy evaluation. Some preclinical testing may continue after submission of the IND. The IND becomes automatically effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless the FDA raises questions or concerns in response to a proposed clinical study and places the study on a clinical hold within the 30-day timeframe. In such a case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding issues before commencing the clinical study. The FDA may impose clinical holds due to safety concerns or non-compliance on all product candidates within a certain pharmaceutical class at any time before or during clinical studies. In addition, the FDA can impose partial clinical holds prohibiting the initiation of clinical studies for a certain dose or of a certain duration.
In accordance with GCP regulations, all clinical studies must be conducted under the supervision of one or more qualified investigators. These regulations require informed consent in writing from all research subjects before their participation in any clinical study. An IRB must review and approve the plan for any clinical study before it commences at any institution, and the IRB must continuously review and re-approve the study at least annually. Among other things, the IRB considers whether the risks to individual participants in the clinical study are minimal and reasonable in relation to the anticipated benefits. The IRB also approves the information regarding the clinical study and the consent form that must be given to each clinical study subject or his or her legal representative. The IRB must also monitor the clinical study until completed. Each new clinical protocol and any amendments thereto must be submitted to the FDA for review, and to the IRB for approval. The protocols detail the objectives of the clinical study, dosing procedures, subject selection and exclusion criteria, and the parameters to be used to monitor subject safety (among other things). Study sites are subject to inspection for compliance with GCP.
Information about certain clinical trials must be submitted within specific timeframes to the National Institutes of Health, for public dissemination on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Human clinical studies are typically conducted in three sequential phases that may overlap or be combined:
| ● | Phase 1. In Phase 1, the product is initially introduced to a limited number of healthy human subjects or patients and is tested for safety, dosage tolerance, absorption, metabolism, distribution and excretion and, if possible, to gain early evidence on effectiveness. In the case of certain products intended to treat severe or life-threatening diseases, particularly when the product is suspected or known to be unavoidably toxic, initial human testing may be conducted in patients. | |
| ● | Phase 2. Phase 2 involves clinical studies in a limited patient population to identify potential adverse effects and safety risks, to preliminarily evaluate the efficacy of the product for specific diseases and to determine dosage tolerance, optimal dosage and schedule. | |
| ● | Phase 3. In Phase 3, clinical studies are conducted on a larger patient population located in geographically dispersed clinical sites to further evaluate the dosage, clinical efficacy and safety of the product. Phase 3 clinical studies are intended to determine the overall risks and benefits of the product and provide an adequate basis for product labeling. |
Progress reports explaining the results of the clinical studies must be submitted to the FDA at least annually. Safety reports must be submitted to the FDA and the investigators for serious and unexpected suspected adverse events. There is no guarantee that Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 testing will be completed successfully within any specified period, if at all. The FDA or the sponsor may suspend or terminate a clinical study at any time for various reasons, including a finding that the research subjects or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Likewise, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical study at its institution if the clinical study is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB’s requirements or if the drug has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients.
| 16 |
U.S. Review and Approval Processes
Upon the successful completion of the required clinical testing, an NDA is submitted to the FDA requesting approval to market the product. The NDA reports the results of product development, preclinical and clinical studies, descriptions of the manufacturing process, analytical tests conducted on the drug, proposed labeling and other relevant information.
In connection with the submission of an NDA, the payment of a substantial application user fee is required (although a waiver is available under limited circumstances, including, for the first human drug application submitted by a small business or its affiliate). The sponsor of an approved NDA is also required to pay annual program user fees.
Under the Pediatric Research Equity Act of 2003, an NDA application (or supplements thereto) for a new active ingredient, new indication, new dosage form, new dosing regimen, or new route of administration must contain adequate data to assess the safety and effectiveness of the drug for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations, and to support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the product is safe and effective, unless the applicant has obtained a waiver or deferral.
In 2012, the Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act amended the FDCA to require submission of an initial Pediatric Study Plan (“PSP”) for any sponsor that plans to submit a marketing application for a drug that includes a new active ingredient, new indication, new dosage form, new dosing regimen or new route of administration. The initial PSP must be submitted within sixty days of an End-of-Phase 2 meeting or as may be agreed between the sponsor and the FDA. The initial PSP must contain an outline of the pediatric study or studies that the sponsor plans to conduct, including study objectives and design, age groups, relevant endpoints and statistical approach, or a justification for not including such detailed information, and any request for a deferral of pediatric assessments or a full or partial waiver of the requirement to provide data from pediatric studies along with supporting information. The FDA may grant deferrals for submission of data or full or partial waivers on its own volition or at the applicant’s request. The FDA and the sponsor must agree on the PSP. A sponsor can amend an initial PSP at any time (even if initially agreed upon) if changes to the pediatric plan must be considered based on data collected from preclinical studies, early phase clinical studies, and/or other clinical development programs.
The FDA may also require a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (“REMS”) to mitigate any identified or suspected serious risks. The REMS typically includes risk minimization tools, medication guides, assessment plans, physician communication plans, and elements to ensure safe use, including restricted distribution methods, and patient registries.
The FDA reviews all NDA’s submitted to ensure they are sufficiently complete for substantive review before it accepts them for filing. Rather than accept an application for filing, the FDA may request additional information. In such a case, an applicant must re-submit the application along with the additional information, which remains subject to further FDA review. Once an application is accepted for filing, the FDA performs an in-depth substantive review to determine whether the product is safe and effective for its intended use.
The FDA may refer the NDA to an advisory committee consisting of experts for review, evaluation and recommendation regarding its approval and any conditions that may apply thereto. The FDA, while not bound by the recommendation of an advisory committee, considers such recommendations when making decisions. Before approving an NDA, the FDA will also inspect one or more clinical sites to ensure clinical data supporting the submission comply with GCP.
The FDA may refuse to approve an NDA if regulatory requirements are not satisfied or additional clinical data and information is required. Even after such data and information is furnished, the FDA may refuse to approve an NDA for failure to satisfy regulatory requirements. Data from clinical studies may not always be conclusive. Moreover, the FDA may disagree with the applicant’s interpretation of the data.
| 17 |
After evaluating an application, the FDA may issue an approval letter or a complete response letter indicating completion of the review cycle. A complete response letter typically sets forth specific conditions that must be satisfied to secure final approval of the application and may require additional clinical or preclinical testing for the FDA to reconsider the application. The FDA may identify minor deficiencies, such as requiring labeling changes, or major deficiencies, such as requiring additional clinical studies. The complete response letter may also recommend actions to ready the application for approval. An applicant can respond to a complete response letter by correcting all deficiencies and re-submitting the application, withdrawing the application or requesting a hearing.
Even after additional information is submitted, the FDA may determine that an application does not satisfy regulatory requirements and reject it. Once all conditions have been met to the FDA’s satisfaction, the FDA will typically issue an approval letter authorizing commercial marketing of the drug with specific prescribing information for specific indications.
Even after regulatory approval is obtained, approval may be restricted to specific diseases and dosages or limited indications for use. Such limitations could affect the commercial value of the product. On the product labeling, the FDA may require certain contraindications, warnings or precautions. In addition, the FDA may require post-approval studies, including Phase 4 clinical studies, to further evaluate safety and effectiveness. The FDA may also require testing and surveillance programs to monitor the safety of approved commercialized products. After approval, certain changes to the approved product remain subject to additional testing requirements, FDA review and approval. Such changes to the approved product include adding new indications, manufacturing changes, and additional labeling claims.
Abbreviated New Drug Applications (“ANDAs”)
Most drug products receive FDA marketing approval pursuant to an NDA for innovator products, or an ANDA for generic products. The Hatch-Waxman amendments to the FDCA established a statutory procedure for submission and FDA review and approval of ANDA’s for generic versions of branded drugs previously approved or listed by the FDA. Because brand companies (otherwise known as “innovators”) have already demonstrated the safety and efficacy of listed drugs, the FDA does not require the same demonstration for generic products. Nevertheless, the FDA requires the manufacturer of generic drugs to perform bioequivalence studies of its test product against the listed drug. The bioequivalence studies for orally administered, systemically available drug products evaluate the rate and extent to which the active pharmaceutical ingredient is absorbed into the bloodstream from the drug product and becomes available at the site of action. Bioequivalence is achieved when there is no significant difference in the rate and extent for absorption of the generic product and the listed drug. An ANDA must contain chemistry, manufacturing, labeling and stability data as well as patent certifications.
Approved products manufactured or distributed in accordance with the FDA regulatory process remain subject to continuing FDA oversight post-approval. Continuing regulatory requirements include periodic reporting, record-keeping, product sampling, product distribution, and advertising and reporting on adverse experiences, deviations, and other issues with the product. In addition, most post-approval changes to the approved product, including adding new indications or other labeling claims, remain subject to prior FDA review and approval. There are also continuing obligations to pay annual user fees for marketed products, as well as new application fees for supplemental applications with clinical data.
The FDA strictly regulates the information presented on products on the market, including information on labeling, advertising, and promotion of products. Products may only be promoted for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved label. The FDA and other agencies actively enforce the rules prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses. A company that improperly promotes off-label uses may be subject to significant liability. Manufacturers must also continue to comply with extensive CGMP regulations, which requires a commitment of time and financial resources. FDA review and approval is generally required for post-approval changes to the manufacturing process and other changes to the approved product, including the addition of new indications and additional labeling claims.
Manufacturers and others involved in the manufacturing and distribution of approved products must register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies. The FDA and state agencies may periodically inspect these establishments, sometimes without prior notice, to ensure compliance with CGMP regulations and other obligations. CGMP requirements apply to all stages of the product manufacturing process, including processing, production, sterilization, packaging, labeling, storage and shipment.
| 18 |
Prior FDA approval is often required for changes to the manufacturing process are implemented. FDA regulations require investigation and correction of departures from CGMP requirements. The FDA may also impose reporting and documentation obligations upon the sponsor and any third party manufacturers used by the sponsor. As a result, to remain compliant with CGMP regulations, manufacturers must continue to commit time, effort and financial resources to production and quality control.
The FDA may impose other post-approval requirements as a condition to approving an application, such as post-marketing testing (including Phase 4 clinical trials) and surveillance to monitor and assess the product’s safety and effectiveness upon commercialization.
The FDA may withdraw approval of a product if an applicant fails to maintain compliance with regulatory requirements or if certain issues arise after the product is introduced to the market. For instance, a subsequent discovery of previously unknown issues, including adverse events of unexpected frequency or severity, problems with the manufacturing process, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, could result in restrictions on the product or a complete withdrawal from the market.
In such cases, potential consequences include revisions to the approved labeling to include new safety information; post-market studies or clinical trials to evaluate new safety risks; and imposition of restrictions under a REMS program. Other potential consequences include:
| ● | Restrictions on the manufacturing or marketing of the product (including complete withdrawal or recall of the product); | |
| ● | Warning letters or holds on post-approval clinical trials; | |
| ● | FDA’s refusal to approve pending NDAs or supplements to approved NDAs; | |
| ● | Suspension or revocation of product license approvals; | |
| ● | Product seizures or detentions; | |
| ● | FDA’s refusal to allow imports or exports of products; or | |
| ● | Civil penalties, criminal penalties or injunctions. |
Manufacturers and distributors must also comply with the Prescription Drug Marketing Act (“PDMA”) and state laws that regulate distribution of prescription products. The PDMA regulates the distribution of prescription drugs, products and product samples at the federal level and sets minimum standards for the registration and regulation of distributors by the states. The PDMA and state laws restrict the distribution of prescription product samples and impose requirements to ensure accountability in distribution.
In addition, new federal legislation and guidance could substantially alter the statutory provisions governing approval, manufacturing and marketing of products regulated by the FDA. New legislation, FDA regulations, guidance, and policies are periodically revised or reinterpreted in ways that could significantly impact our business and our products. We cannot predict the enactment, implementation and potential consequences of any future legislative, regulatory or policy changes.
| 19 |
Pharmaceutical Coverage, Pricing and Reimbursement
In the United States, commercial sales of any products subject to regulatory approval could be conditioned on whether third-party payors (such as government authorities, managed care providers, private health insurers and other organizations) are able to provide coverage and reimbursement in connection with the products.
Coverage and reimbursement of costs are areas of significant uncertainty for any products subject to regulatory approval. The process for determining coverage versus reimbursement may vary widely among third-party payors. Third-party payors may also impose additional requirements on and restrictions to coverage and reimbursement, which could influence the purchase of certain healthcare services and products.
Third-party payors may limit coverage to specific drugs on an approved list, or formulary, which could omit some FDA-approved drugs for a particular indication. Third-party payors may also place drugs at certain formulary levels that result in a lower reimbursement and higher cost-sharing obligation for patients. A third-party payor’s decision to provide coverage for a product may not necessarily imply approval of an adequate reimbursement rate. In addition, the unavailability of third-party reimbursement may affect our ability to maintain price levels sufficient to realize an appropriate return on our investment in product development. Coverage by one third-party payor may not necessarily indicate or imply coverage or reimbursement by other third-party payors. Also, the level or scope of coverage and reimbursement may vary significantly among third-party payors. In addition to scrutinizing the safety and efficacy of medical products and services, third-party payors have increasingly begun to examine and challenge the price, cost-effectiveness and necessity of certain products and services. Thus, to obtain and maintain coverage and reimbursement for any products approved for sale, the conducting of expensive pharmacoeconomic studies may be required to demonstrate the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of such products. There is a chance that third-party payors may not consider our product medically necessary or cost-effective. If third-party payors make such a determination, they may not cover the product after approval as a benefit under their plans. If third-party payors do cover the product, the returns from sales of our product may not sufficiently yield a profit.
Furthermore, federal and state governmental authorities have increasingly shown an interest in implementing cost containment programs to limit government-paid healthcare costs. Such cost containment programs include restrictions on coverage and reimbursement, price controls and requirements to substitute branded prescription drugs with generic products. The adoption and expansion of such restrictive policies and controls could impose limitations or exclusions from coverage for our product.
In the United States, we expect third-party payors and government authorities to increase emphasis on managed care and cost containment measures, which will impact the pricing and coverage for pharmaceutical products. Coverage policies and third-party reimbursement rates may change at any time. Even if we achieve favorable coverage and reimbursement status for an approved product, less favorable coverage policies and reimbursement rates could still be implemented in the future.
Protection of Intellectual Property
We strive to protect our intellectual property in a variety of ways to promote the development of our product candidate and business. Our strategy to safeguard this intellectual property includes the following:
● Patents and patent applications. We are in the process of obtaining method of use patents intended to cover our ANEB-001 product candidate, which are important to the development of our business. We have filed two patent applications for various methods of use of the ANEB-001 compound and delivery systems, which applications are currently pending before the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. We intend to pursue foreign jurisdictions for these patent applications at the relevant time. The patents are expected to expire in 2040.
| 20 |
● Regulatory exclusivity. We could obtain regulatory exclusivity in the United States upon receiving approval of our NDA from the FDA. Upon approval of a new chemical entity (“NCE”), which is a drug that contains no active moiety that has been approved by the FDA in any other NDA, that drug receives five years of marketing exclusivity during which the FDA may not approve a generic version of the drug. In addition, in seeking approval for a drug through an NDA, applicants are required to list with the FDA each patent whose claims cover the applicant’s product. Upon approval of a drug, each of the patents listed in the application for the drug is then published in the FDA’s Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations, commonly known as the Orange Book. Drugs listed in the Orange Book can, in turn, be cited by potential generic competitors in support of approval of an ANDA and then later challenged pursuant to a paragraph IV certification. As part of the Paragraph IV certification process, an NDA holder may initiate a patent infringement lawsuit against the ANDA applicant. The filing of a patent infringement lawsuit by an NDA holder automatically prevents the FDA from approving the ANDA until the earlier of 30 months, expiration of the Orange Book-listed patent, settlement of the lawsuit, or a decision in the infringement case that is favorable to the ANDA applicant. Finally, we could receive an orphan drug designation, which would grant a total of seven years of marketing exclusivity in the United States under the US Orphan Drug Act of 1983, or pediatric drug designation, which provides NDA holders (under the Best Pharmaceuticals for Children Act (BPCA)) a six-month extension of any exclusivity (patent or non-patent) for a drug.
● Trade secrets. We rely on trade secret laws of general applicability for aspects of our business that are not readily amenable to or appropriate for patent protection.
● Confidentiality agreements. We rely upon confidentiality agreements signed by our employees, consultants and third parties.
● License agreement. We have entered into an exclusive worldwide licensing agreement with Vernalis to develop, strengthen and commercialize our ANEB-001 compound. This exclusive in-licensing opportunity allows us to maintain and enhance our proprietary position in ANEB-001.
● Trademarks. We use “Anebulo” as our trademark. As we develop our drug candidate and business, we intend to add trademarks to our portfolio of intellectual property.
We believe these methods provide us material defensibility around our core intellectual property.
Recent Developments
On September 10, 2021, we completed finished product manufacturing of our lead drug ANEB-001 for use in our upcoming Phase 2 clinical study. In compliance with all current Good Manufacturing Practice requirements, ANEB-001’s active pharmaceutical ingredient was delivered to its contract manufacturer and filled into 10mg and 50mg capsules for finished product. We are on track to commence our Phase 2 proof-of-concept study in October 2021, which is ahead of schedule, and we expect initial topline results from the first cohort in the first half of calendar 2022.
Employees
As of June 30, 2021, we had two full-time employees and one part-time employee, none of whom were covered by collective bargaining agreements. In addition, we have a number of outside consultants that are not on our payroll who are involved directly in scientific research and development activities. We believe that relations with our employees are generally good.
Corporate Information
We were incorporated in Delaware in April 2020. Our principal executive offices are located at 1415 Ranch Road 620 South, Suite 201, Lakeway, Texas 78734, and our telephone number is 512-598-0931.
Available Information
Our website address is www.anebulo.com, which includes a section for investor relations. Information on our website is not incorporated by reference herein. We will make available on our website, free of charge, our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. The SEC maintains an Internet site (http://www.sec.gov) containing reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC.
| 21 |
The following risk factors and other information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K should be carefully considered. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones we face. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we presently deem less significant may also impair our business operations. If any of the following risks occur, our business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth prospects could be materially and adversely affected.
Risks Related to our Business, Financial Condition and Capital Requirements
We have not generated any revenue since our inception and expect to incur future losses and may never become profitable.
We have not generated any revenue. As of June 30, 2021, we have an accumulated deficit of $38,644,084, which includes $3,787,104 of operating losses incurred since inception. The likelihood of our future success must be considered in light of the expenses, difficulties, complications and delays often encountered in connection with the clinical trials that will be conducted and on the development of new solutions to common addictions. These potential challenges include unanticipated clinical trial delays, poor data, changes in the regulatory and competitive landscape and additional costs and expenses that may exceed current budget estimates. In order to complete certain clinical trials and otherwise operate pursuant to our current business strategy, we anticipate that we will incur increased operating expenses. In addition, we expect to incur significant losses and experience negative cash flow in the future as we fund the operating losses and capital expenditures. We recognize that if we are unable to generate sufficient revenues or source funding, we will not be able to continue operations as currently contemplated, complete planned clinical trials and/or achieve profitability. Our failure to achieve or maintain profitability will also negatively impact the value of our shares. If we are unsuccessful in addressing these risks, then we may need to curtail our business activities.
The future success of our business cannot be determined at this time, and we do not anticipate generating revenue from product sales in the near term. In addition, we have no experience in commercializing drug products on our own and face a number of challenges with respect to commercialization efforts, including, among other challenges:
| ● | having inadequate financial or other resources to complete the development of our product candidate; | |
| ● | the inability to manufacture our product in commercial quantities, at an adequate quality, at an acceptable cost or in collaboration with third parties; | |
| ● | experiencing delays or unplanned expenditures in product development, clinical testing or manufacturing; | |
| ● | the inability to establish adequate sales, marketing and distribution channels; | |
| ● | healthcare professionals may not adopt and patients may not accept our drug, if approved for marketing; | |
| ● | we may not be aware of possible complications or other side effects from the use of our product since we have limited clinical experience with respect to the actual effects from use of our product; | |
| ● | technological breakthroughs in reversing ACIs and treating patients experiencing intoxication symptoms may reduce the demand for our product, if it develops; | |
| ● | changes in the market for reversing ACIs and treating patients experiencing intoxication symptoms, new alliances between existing market participants and the entrance of new market participants may interfere with our market penetration efforts; | |
| ● | third-party payors may not agree to reimburse patients for any or all of the purchase price of our product, which may adversely affect patients’ willingness to use our product; | |
| ● | uncertainty as to market demand may result in inefficient pricing of our product; | |
| ● | we may face third-party claims of intellectual property infringement; | |
| ● | we may fail to obtain or maintain regulatory approvals for our product in our markets or may face adverse regulatory or legal actions relating to our product even if regulatory approval is obtained; and | |
| ● | we are dependent upon the results of clinical studies relating to our product and the products of our competitors. If data from a clinical trial is unfavorable, we would be reluctant to advance the product for the indication for which it was being developed. |
| 22 |
If we are unable to meet any one or more of these challenges successfully, our ability to effectively commercialize our products could be limited, which in turn could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We currently rely on a license from a third party, and in the future may rely on additional licenses from other third parties, in relation to our development of ANEB-001, and if we fail to comply with our obligations under our current or future intellectual property license agreements or otherwise experience disruptions to our business relationships with our current or any future licensors, we could lose intellectual property rights that are important to our business.
We are, and expect to continue to be, reliant upon third-party licensors for certain patent and other intellectual property rights that are important or necessary to the development of our product candidates, including ANEB-001. On May 26, 2020, we entered into a License Agreement with Vernalis, pursuant to which Vernalis granted to us an exclusive license to develop and commercialize our ANEB-001 product candidate. Under the License Agreement, we have the sole discretion to carry out the development and commercialization of ANEB-001, including obtaining regulatory approvals. We retain the sole right over certain patent rights (including patent applications) and know-how controlled by us that are necessary or reasonably useful to developing and commercializing the licensed product during the term of the License Agreement. The License Agreement imposes, and we expect that any future license agreement will impose, specified diligence, milestone payment, royalty, commercialization, development and other obligations on us and require us to meet development timelines, or to exercise diligent or commercially reasonable efforts to develop and commercialize licensed products, in order to maintain the license.
Furthermore, our licensors have, or may have in the future, the right to terminate a license if we materially breach the agreement and fail to cure such breach within a specified period or in the event we undergo certain bankruptcy events. In spite of our best efforts, our current or any future licensors might conclude that we have materially breached our license agreements and might therefore terminate the license agreements. If our license agreements are terminated, we may lose our rights to develop and commercialize product candidates and technology, lose patent protection, experience significant delays in the development and commercialization of our product candidates and technology, and incur liability for damages. If these in-licenses are terminated, or if the underlying intellectual property fails to provide the intended exclusivity, our competitors or other third parties could have the freedom to seek regulatory approval of, and to market, products and technologies identical or competitive to ours and we may be required to cease our development and commercialization of certain of our product candidates and technology. In addition, we may seek to obtain additional licenses from our licensors and, in connection with obtaining such licenses, we may agree to amend our existing licenses in a manner that may be more favorable to the licensors, including by agreeing to terms that could enable third parties, including our competitors, to receive licenses to a portion of the intellectual property that is subject to our existing licenses and to compete with any product candidates we may develop and our technology. Any of the foregoing could have a material adverse effect on our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Our License Agreement with Vernalis continues for an indefinite term and terminates, among other ways, under the following circumstances: (i) on its terms when royalties and other sums cease to be payable thereunder; (ii) by us at any time by providing 60 days’ prior notice; or (iii) upon an event of default, such as a material breach or insolvency of the other party. Upon termination, all rights and licenses granted by Vernalis will revert immediately to Vernalis; all outstanding sums as of the termination date will be immediately due and payable to Vernalis; and we will return or destroy, at Vernalis’s request, any regulatory or other materials provided by Vernalis pursuant to the License Agreement.
Disputes may also arise between us and Vernalis or future licensors regarding intellectual property subject to a license agreement, including:
| ● | the scope of rights granted under the license agreement and other interpretation-related issues; | |
| ● | our financial or other obligations under the license agreement; | |
| ● | whether, and the extent to which, our products, technology and processes infringe on intellectual property of the licensor that is not subject to the licensing agreement; | |
| ● | our diligence obligations under the license agreement and what activities satisfy those diligence obligations; | |
| ● | the inventorship and ownership of inventions and know-how resulting from the joint creation or use of intellectual property by our licensor(s); and | |
| ● | the priority of invention of patented technology. |
| 23 |
If we do not prevail in such disputes, we may lose any or all of our rights under such license agreements, experience significant delays in the development and commercialization of our products and technologies, or incur liability for damages, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects. In addition, we may seek to obtain additional licenses from our licensor(s) and, in connection with obtaining such licenses, we may agree to amend our existing licenses in a manner that may be more favorable to the licensor(s), including by agreeing to terms that could enable third parties, including our competitors, to receive licenses to a portion of the intellectual property that is subject to our existing licenses and to compete with our products.
In addition, the agreements under which we currently and in the future license intellectual property or technology from third parties are complex and certain provisions in such agreements may be susceptible to multiple interpretations. The resolution of any contract interpretation disagreement that may arise could narrow what we believe to be the scope of our rights to the relevant intellectual property or technology, or increase what we believe to be our financial or other obligations under the relevant agreement, either of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. Moreover, if disputes over intellectual property that we have licensed prevent or impair our ability to maintain our current licensing arrangements on commercially acceptable terms, we may be unable to successfully develop and commercialize any affected products or services, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Absent the license agreements, we may infringe patents subject to those agreements, and if the license agreements are terminated, we may be subject to litigation by the licensor. Litigation could result in substantial costs to us and distract our management. If we do not prevail, we may be required to pay damages, including treble damages, attorneys’ fees, costs and expenses and royalties or be enjoined from selling ANEB-001, which could adversely affect our ability to offer products or services, our ability to continue operations and our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We currently have no product revenue and will need to raise additional capital in the future, which may be unavailable to us or may cause dilution or place significant restrictions on our ability to operate.
We may be unable to generate sufficient revenue or cash flow to fund our operations. We will need to seek additional equity or debt financing to provide the capital required to maintain or expand our operations, continue the development of our product candidate, build our sales and marketing capabilities, promote brand identity, develop or acquire complementary technologies, products or businesses, or provide for our working capital requirements and other operating and general corporate purposes.
We currently do not have any arrangements or credit facilities as a source of funds, and we make no assurance that we will be able to raise sufficient additional capital in the future if needed on acceptable terms, or at all. If such financing is not available on satisfactory terms, or is not available at all, we may be required to delay, scale back or eliminate the development of our current product or future candidates and other business. This may materially adversely affect our operations and financial condition as well as our ability to achieve business objectives and maintain competitiveness.
If we raise additional capital by issuing equity securities and/or equity-linked securities, the percentage ownership of our existing stockholders may be reduced, and accordingly these stockholders may experience substantial dilution. We may also issue equity securities and/or equity-linked securities that provide for rights, preferences and privileges senior to those of our common stock. Given our need for cash and that equity and equity-linked issuances are very common types of fundraising for companies like us, the risk of dilution is particularly significant for our stockholders.
Debt financing, if obtained, may involve agreements that include liens on our assets and covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions such as incurring additional debt. Debt financing could also be required to be repaid regardless of our operating results.
| 24 |
If we raise additional funds through collaborations and licensing arrangements, we may be required to relinquish some rights to our current or future products or to grant licenses on terms that are not favorable to us.
We have limited operating history as a publicly-traded company, and our inexperience could materially and adversely affect us and our stockholders.
We became a public company in May 2021 and, therefore, we have limited operating history as a publicly traded company. Our board of directors and management team have overall responsibility for our management. As a publicly-traded company, we are required to develop and implement substantial control systems, policies and procedures in order to satisfy our periodic SEC reporting and Nasdaq obligations. We cannot assure you that management’s past experience will be sufficient to successfully develop and implement these systems, policies and procedures and to operate our company. Failure to do so could jeopardize our status as a public company, and the loss of such status may materially and adversely affect us and our stockholders.
We depend on third parties in connection with our preclinical testing and clinical trials, which may result in costs and delays that prevent us from obtaining regulatory approval or successfully commercializing ANEB-001 or future product candidates.
We engage third parties to perform various aspects of our preclinical testing and clinical trials. We have entered into agreements with third parties, including Traxeus, Aptuit (Verona) SRL, and Centre for Human Drug Research, which provide certain pharmaceutical research and development services to us. We depend on these third parties to perform these activities on a timely basis in accordance with the protocol, good laboratory practices, good clinical practices and other regulatory requirements. Our reliance on these third parties for preclinical and clinical development activities reduces our control over these activities. Accordingly, if these parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or obligations or meet expected deadlines, our preclinical testing and clinical trials may be extended, delayed, terminated or our data may be rejected by the FDA. If there are delays in testing or obtaining regulatory approvals as a result of a third party’s failure to perform, our drug discovery and development costs will likely increase, and we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or successfully commercialize our current or future product candidates.
Third parties’ abilities to adequately and timely manufacture and supply our current or future product candidates is dependent on the operation of their facilities which may be impacted by, among other things:
| ● | availability, performance or contamination of raw materials and components used in the manufacturing process, particularly those for which we have no other source or supplier; | |
| ● | capacity of their facilities; | |
| ● | the performance of information technology systems; | |
| ● | compliance with regulatory requirements; | |
| ● | inclement weather and natural disasters; | |
| ● | changes in forecasts of future demand for product components; | |
| ● | timing and actual number of production runs for product components; | |
| ● | potential facility contamination by microorganisms or viruses; | |
| ● | updating of manufacturing specifications; and | |
| ● | product quality success rates and yields. |
If the efficient manufacture and supply of our current or future product candidates is interrupted, we may experience delayed shipments or supply constraints, which may materially impact our ongoing and future preclinical testing and clinical trials.
Any contract manufacturer must undergo a potentially lengthy FDA approval process, as well as other regulatory approval processes, and are subject to continued review by the FDA and other regulatory authorities. If we or our third-party service providers cease or interrupt production or if our third-party service providers fail to supply materials, products or services to us, we may experience delayed shipments, and supply constraints for our current or future product candidates.
Public health epidemics, pandemics or outbreaks, including the recent novel coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19), could adversely affect our business.
In December 2019, the novel coronavirus (“COVID-19”) was identified in Wuhan, China. The virus continues to spread globally, has been declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization and has spread to over 100 countries, including the United States. The COVID-19 outbreak is significantly affecting our communities, our business operations and the business operations of the CROs and CMOs we have engaged, as well as the U.S. economy and financial markets. The full extent to which the COVID-19 outbreak will impact our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows will depend on future developments that are highly uncertain and cannot be accurately predicted, including new information that may emerge concerning COVID-19 and the actions to contain it or treat its impact and the economic impact on local, regional, national and international markets. As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows are likely to be materially adversely affected, particularly if the pandemic persists for a significant amount of time.
COVID-19 or other public health epidemics, pandemics or outbreaks, and the resulting business or economic disruptions resulting therefrom, may adversely impact our business as well as our ability to raise capital. The impact of this pandemic has been and will likely continue to be extensive in many aspects of society, which has resulted in and will likely continue to result in significant disruptions to the global economy, as well as businesses and capital markets around the world.
While we cannot presently predict the scope and severity of any potential business shutdowns or disruptions, if we or any of our business partners, clinical trial sites, distributors and other third parties with whom we conduct business, were to experience shutdowns or other business disruptions, our ability to conduct our business in the manner and on the timelines presently planned could be materially and negatively impacted. For example, if our development program for cannabinoid overdoses were to be delayed, it may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
| 25 |
The pandemic’s impact on the medical community and the global economy could have an adverse impact on future sales upon which we expect to derive royalties and milestones, which could lead to a decrease in our revenues, net income and assets.
Several measures have been and are currently being implemented by the United States and other governments to address the current COVID-19 pandemic and its economic impacts. At this time, it is impossible to predict the success of these measures and whether or not they will have unforeseen negative consequences for our business. In addition, our results of operations, financial position and cash flows may be adversely affected by federal or state laws, regulations, orders, or other governmental or regulatory actions addressing the current COVID-19 pandemic or the U.S. healthcare system, which, if adopted, could result in direct or indirect restrictions to our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flow.
The foregoing and other continued disruptions to our business as a result of COVID-19 could result in a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Further, the COVID-19 pandemic could heighten the risks in certain of the other risk factors described herein.
Risks Related to our Internal Control
If we fail to establish and maintain proper and effective internal control over financial reporting, our operating results and our ability to operate our business could be harmed.
Ensuring that we have adequate internal control over financial reporting in place so that we can produce accurate financial statements on a timely basis is a costly and time-consuming effort that needs to be re-evaluated frequently. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. In connection with our initial public offering (the “IPO”), we began the process of documenting, reviewing, and improving our internal controls and procedures for compliance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (the “Sarbanes-Oxley Act”), which will require annual management assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. We have begun recruiting additional finance and accounting personnel with certain skill sets that we will need as a public company. If we are not able to comply with the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act in a timely manner, or if we are unable to maintain proper and effective internal controls, we may not be able to produce timely and accurate financial statements. If that were to happen, the market price of our stock could decline and we could be subject to sanctions or investigations by the stock exchange on which our common stock is listed, the SEC or other regulatory authorities.
Implementing any appropriate changes to our internal controls may distract our officers and employees, entail substantial costs to modify our existing processes, and take significant time to complete. These changes may not, however, be effective in maintaining the adequacy of our internal controls, and any failure to maintain that adequacy, or consequent inability to produce accurate financial statements on a timely basis, could increase our operating costs and harm our business. In addition, investors’ perceptions that our internal controls are inadequate or that we are unable to produce accurate financial statements on a timely basis may harm our stock price and make it more difficult for us to effectively market and sell our service to new and existing customers.
Risks Related to our Intellectual Property
If we are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection for important aspects of ANEB-001, or if the scope of the patent protection obtained is not sufficiently broad, our competitors could develop and commercialize products that are similar or identical to ours, and our ability to successfully commercialize our current or future product candidates may be adversely affected.
Our commercial success will depend, in part, on our ability to obtain and maintain patent protection in the United States and other countries with respect to ANEB-001, our product candidate. We seek to protect our proprietary position by filing patent applications in the United States and abroad related to aspects of our product candidate that are important to our business. Given that the development of our product candidates is at an early stage, our intellectual property portfolio with respect to certain aspects of our product candidates is also at an early stage. For example, we have filed or intend to file patent applications related to aspects of ANEB-001, our product candidate; however, there can be no assurance that any such patent applications will issue as granted patents around the world. The requirements for patentability differ in certain countries, and certain countries have heightened requirements for patentability. Further, in some cases, we have only filed provisional patent applications on certain aspects of our technology and product candidate, and provisional patent applications are not eligible to become an issued patent until, among other things, we file a non-provisional patent application within 12 months of the filing date of the applicable provisional patent application. Any failure to file a non-provisional patent application within this timeline could cause us to lose the ability to obtain patent protection for the inventions disclosed in the associated provisional patent applications.
| 26 |
Further, any changes we make to our product candidates to cause them to have what we view as more advantageous properties may not be covered by our existing patent applications, and we may be required to file new applications and/or seek other forms of protection for any such altered product candidates. There can be no assurance that we would be able to secure patent protection that would adequately cover any such altered product candidates. There can also be no assurance that any such patent applications will be issued as granted patents, and even if they do issue, such patent claims may be insufficient to prevent third parties, such as our competitors, from utilizing our technology. Any failure to obtain or maintain patent protection related to aspects of our product candidates could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects.
Even if we obtain issued or granted patents with respect to our product candidates, we cannot be certain that such patents will not later be found to be invalid and/or unenforceable. Currently, we do not have patents on our core intellectual property.
The patent prosecution process is expensive and time-consuming, and we may not be able to file and prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner. It is also possible that we will fail to identify patentable aspects of our research and development output before it is too late to obtain patent protection. Although we may enter into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to patentable aspects of our research and development output, such as our employees, distribution partners, consultants, advisors and other third parties, any of these parties may breach the agreements and disclose such output before a patent application is filed, thereby jeopardizing our ability to seek patent protection.
The patent position of pharmaceutical companies generally is highly uncertain, involves complex legal and factual questions and has in recent years been the subject of much litigation. As a result, the issuance, scope, validity, enforceability and commercial value of our potential patent rights are highly uncertain. Our pending and future patent applications may not result in patents being issued, and even if issued, the patents may not meaningfully protect our current or future product candidates, effectively prevent competitors and third parties from commercializing competitive products or otherwise provide us with any competitive advantage. Our competitors or other third parties may be able to circumvent our patents by developing similar or alternative products in a non-infringing manner.
Moreover, the coverage claimed in a patent application can be significantly reduced before the patent is issued, and its scope can be reinterpreted after issuance. Patent applications we own currently or that in the future issue as patents may not be issued in a form that will provide us with any meaningful protection, prevent competitors or other third parties from competing with us, or otherwise provide us with any competitive advantage. Any patents to which we have rights may be challenged, narrowed, circumvented, or invalidated by third parties. Consequently, we do not know whether our product candidates will be protectable or remain protected by valid and enforceable patents.
The issuance of a patent is not conclusive as to its inventorship, scope, validity, or enforceability, and our patents may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the United States and abroad. We may be subject to a third-party pre-issuance submission of prior art to the United States Patent and Trademark Office (the “USPTO”) or post-issuance become involved in opposition, derivation, revocation, reexamination, post-grant and inter partes review, or interference proceedings or other similar proceedings challenging our patent rights. An adverse determination in any such submission, proceeding, or litigation could reduce the scope of, or invalidate or render unenforceable, such patent rights, allow third parties to commercialize our product candidates or other technologies and compete directly with us, without payment to us, or result in our inability to manufacture or commercialize products without infringing third-party patent rights. Moreover, we may have to participate in interference proceedings declared by the USPTO to determine priority of invention or in post-grant challenge proceedings, such as post-grant review at the USPTO or oppositions in a foreign patent office, that challenge our priority of invention or other features of patentability with respect to our patents and patent applications. Such challenges may result in loss of patent rights, loss of exclusivity, or in patent claims being narrowed, invalidated, or held unenforceable, which could limit our ability to stop others from using or commercializing similar or identical technology and products, or limit the duration of the patent protection of our product candidates and other technologies. Such proceedings also may result in substantial cost and require significant time from our scientists and management, even if the eventual outcome is favorable to us.
| 27 |
If we are unsuccessful in any such proceeding or other priority or inventorship dispute, we may be required to obtain licenses from third parties, including parties involved in any such interference proceedings or other priority or inventorship disputes. Such licenses may not be available on commercially reasonable terms or at all, or may be non-exclusive. If we are unable to obtain and maintain such licenses, we may need to cease the development, manufacture, and commercialization of one or more of the product candidates we may develop. Termination of these licenses or reduction or elimination of our rights under these licenses may result in our having to negotiate new or reinstated agreements with less favorable terms, or cause us to lose our rights under these licenses, including our rights to important intellectual property or technology. The loss of exclusivity or the narrowing of our owned and licensed patent claims could limit our ability to stop others from using or commercializing similar or identical technology and products.
In addition, given the amount of time required for the development, testing, and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such product candidates might expire before or shortly after such product candidates are commercialized. As a result, our intellectual property may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing products similar or identical to ours.
Some of our patents and patent applications may in the future be co-owned with third parties. In addition, future collaborators or licensors may co-own their patents and patent applications with other third parties with whom we do not have a direct relationship. Our rights to certain of these patents and patent applications may be dependent, in part, on inter-institutional or other operating agreements between the joint owners of such patents and patent applications, who are not parties to our license agreements. If our future collaborators or licensors do not have exclusive control of the grant of licenses under any such third-party co-owners’ interest in such patents or patent applications or we are otherwise unable to secure such exclusive rights, such co-owners may be able to license their rights to other third parties, including our competitors, and our competitors could market competing products and technology to the extent such products and technology are not also covered by our intellectual property. In addition, we may need the cooperation of any such co-owners of our patents in order to enforce such patents against third parties, and such cooperation may not be provided to us.
We cannot be certain that our potential patent rights will be effective in protecting ANEB-001 and related technologies. Failure to protect such assets may have a material adverse effect on our business, operations, financial condition and prospects.
If we do not obtain patent term extension and data exclusivity for any product candidates we may develop, our business may be materially harmed.
Depending upon the timing, duration, and specifics of any FDA marketing approval of ANEB-001 and related technologies we may develop, one or more of our U.S. patents may be eligible for limited patent term extension under the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984 (the “Hatch-Waxman Act”). The Hatch-Waxman Act permits a patent term extension of up to five years as compensation for patent term lost during the FDA regulatory review process. A patent term extension cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the date of product approval, only one patent may be extended and only those claims covering the approved drug, a method for using it, or a method for manufacturing it may be extended. Similar extensions as compensation for patent term lost during regulatory review processes are also available in certain foreign countries and territories, such as in Europe under a Supplementary Patent Certificate. However, we may not be granted an extension in the United States and/or foreign countries and territories because of, for example, failing to exercise due diligence during the testing phase or regulatory review process, failing to apply within applicable deadlines, failing to apply prior to expiration of relevant patents, or otherwise failing to satisfy applicable requirements. Moreover, the applicable time period or the scope of patent protection afforded could be less than we request. If we are unable to obtain patent term extension or the term of any such extension is shorter than what we request, our competitors may obtain approval of competing products following our patent expiration, and our business, financial condition, results of operations, and growth prospects could be materially harmed.
| 28 |
We may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights throughout the world, which could negatively impact our business.
Filing, prosecuting and defending patent rights on important aspects of ANEB-001 in all countries throughout the world would be prohibitively expensive, and our intellectual property rights in some countries outside the United States can be less extensive than those in the United States. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as federal and state laws in the United States. Further, licensing partners may not prosecute patents in certain jurisdictions in which we may obtain commercial rights, thereby precluding the possibility of later obtaining patent protection in these countries. Consequently, we may not be able to prevent from selling or importing products made using our inventions in and into the United States or other jurisdictions. Competitors may develop their own products and may also export infringing products to territories where we may have patent protection, but enforcement is not as strong as that in the United States. These products may compete with ANEB-001, and our patent or other intellectual property rights may not be effective or sufficient to prevent them from competing.
Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting and defending intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of certain countries, particularly certain developing countries, do not favor the enforcement of patents, trade secrets and other intellectual property protection, particularly those relating to biotechnology products, which could make it difficult for us to stop the infringement of our patent rights or marketing of competing products in violation of our proprietary rights generally. We may not prevail in any lawsuits that we initiate and the damages or other remedies awarded, if any, may not be commercially meaningful. Furthermore, while we intend to protect our intellectual property rights in our expected significant markets, we cannot ensure that we will be able to initiate or maintain similar efforts in all jurisdictions in which we may wish to market our current or future product candidates. Accordingly, our efforts to protect our intellectual property rights in such countries may be inadequate, which may have an adverse effect on our ability to successfully commercialize our current or future product candidates in all of our expected significant foreign markets.
Many countries have compulsory licensing laws under which a patent owner may be compelled to grant licenses to third parties. In addition, many countries limit the enforceability of patents against government agencies or government contractors. In these countries, the patent owner may have limited remedies, which could materially diminish the value of such patent. If we or any of our future collaborators or licensors is forced to grant a license to third parties with respect to any patents relevant to our business, our competitive position may be impaired, and our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects may be adversely affected. Changes in patent law in the United States and other jurisdictions could diminish the value of patents in general, thereby impairing our ability to protect our products.
Changes in either the patent laws or interpretation of the patent laws in the United States or other jurisdictions could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of patent applications and the enforcement or defense of issued patents. Assuming that other requirements for patentability are met, prior to March 16, 2013, in the United States, the first to invent the claimed invention was entitled to the patent, while outside the United States, the first to file a patent application was entitled to the patent. On or after March 16, 2013, under the Leahy-Smith America Invents Act (the “America Invents Act”) enacted on September 16, 2011, the United States transitioned to a first inventor to file system in which, assuming that other requirements for patentability are met, the first inventor to file a patent application will be entitled to the patent on an invention regardless of whether a third-party was the first to invent the claimed invention. A third-party that files a patent application in the USPTO on or after March 16, 2013, but before us could therefore be awarded a patent covering an invention of ours even if we had made the invention before it was made by such third-party. This will require us to be cognizant going forward of the time from invention to filing of a patent application. Since patent applications in the United States and most other countries are confidential for a period of time after filing or until issuance, we cannot be certain that we were the first to either (i) file any patent application related to ANEB-001 or (ii) invent any of the inventions claimed in our patents or patent applications.
| 29 |
The America Invents Act also includes a number of significant changes that affect the way patent applications will be prosecuted and also may affect patent litigation. These include allowing third-party submission of prior art to the USPTO during patent prosecution and additional procedures to attack the validity of a patent by USPTO administered post-grant proceedings, including post-grant review, inter partes review, and derivation proceedings. Because of a lower evidentiary standard in USPTO proceedings compared to the evidentiary standard in United States federal courts necessary to invalidate a patent claim, a third-party could potentially provide evidence in a USPTO proceeding sufficient for the USPTO to hold a claim invalid even though the same evidence would be insufficient to invalidate the claim if first presented in a district court action. Accordingly, a third-party may attempt to use the USPTO procedures to invalidate our patent claims that would not have been invalidated if first challenged by the third-party as a defendant in a district court action. Therefore, the America Invents Act and its implementation could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of our patent applications and the enforcement or defense of our issued patents, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects.
In addition, the patent positions of companies in the development and commercialization of biopharmaceuticals are particularly uncertain. Recent U.S. Supreme Court rulings have narrowed the scope of patent protection available in certain circumstances and weakened the rights of patent owners in certain situations. This combination of events has created uncertainty with respect to the validity and enforceability of patents, once obtained. Depending on future actions by the U.S. Congress, the federal courts, and the USPTO, the laws and regulations governing patents could change in unpredictable ways that could have a material adverse effect on our existing patent portfolio and our ability to protect and enforce our intellectual property in the future.
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our trade secrets, the value of our technology could be materially adversely affected and our business would be harmed.
In addition to seeking patents for important aspects of ANEB-001, we also rely on trade secrets, including unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary information, in seeking to develop and maintain a competitive position. We seek to protect these trade secrets, in part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to them, such as our employees, consultants, independent contractors, advisors, corporate collaborators, outside scientific collaborators, contract manufacturers, suppliers and other third parties. Monitoring unauthorized uses and disclosures is difficult, and we do not know whether the steps we have taken to protect our proprietary technologies will be effective.
While we seek to protect these trade secrets and other proprietary technology, we cannot guarantee that our trade secrets and other proprietary and confidential information will not be disclosed or that competitors will not otherwise gain access to our trade secrets. Any party with whom we have executed such an agreement may breach that agreement and disclose our proprietary information, including our trade secrets, and we may not be able to obtain adequate remedies for such breaches. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, some courts both within and outside the United States may be less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets. Further, if any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor, we would have no right to prevent such third party, or those to whom they communicate such technology or information, from using that technology or information to compete with us. If any of our trade secrets were to be disclosed to or independently developed by a competitor, our business and competitive position could be harmed.
Trade secrets and know-how can be difficult to protect as trade secrets and know-how will over time be disseminated within the industry through independent development, the publication of journal articles, and the movement of personnel skilled in the art from company to company or academic to industry scientific positions. If we fail to prevent material disclosure of the know-how, trade secrets and other intellectual property related to our technologies to third parties, we will not be able to establish or maintain a competitive advantage in our market, which could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. Even if we are able to adequately protect our trade secrets and proprietary information, our trade secrets could otherwise become known or could be independently discovered by our competitors. For example, competitors could purchase our product and attempt to replicate some or all of the competitive advantages we derive from our development efforts, design around our protected technology or develop their own competitive technologies that fall outside of our intellectual property rights. If any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor, in the absence of patent protection, we would have no right to prevent them, or those to whom they communicate, from using that technology or information to compete with us.
| 30 |
We may not be able to prevent misappropriation of our intellectual property, trade secrets or confidential information, particularly in countries where the laws may not protect those rights as fully as in the United States. Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, there is a risk that some of our confidential information could be compromised by disclosure during this type of litigation.
The expiration or loss of patent protection may adversely affect our future revenues and operating earnings.
Patent protection is important in the development and eventual commercialization of our product candidate. Patents covering our product candidate normally provide market exclusivity, which is important in order for our product candidate to become profitable. Even if we are successful in obtaining a patent, patents have a limited lifespan. In the United States, the natural expiration of a utility patent is generally 20 years after it is filed. Various extensions may be available; however, the life of a patent, and the protection it affords, is limited. Without patent protection, we may be open to competition from generic versions of such compositions, methods and devices. As a result, our owned and licensed patent portfolio may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing products similar to ours.
Risks Related to Product Development, Regulatory Approval, Manufacturing and Commercialization
Delays in the completion of, or the termination of, a clinical trial for ANEB-001, our lead drug candidate, could adversely affect our business.
Clinical trials are very expensive, time-consuming, unpredictable and difficult to design and implement. The results of clinical trials may be unfavorable, they may continue for several years, and they may take significantly longer to complete and involve significantly more costs than expected. Delays in the commencement or completion of clinical testing could significantly affect product development costs and plans with respect to our drug candidate. The commencement and completion of clinical trials can be delayed and experience difficulties for a number of reasons, including delays and difficulties caused by circumstances over which we may have no control. For instance, approvals of the scope, design or trial site may not be obtained from the FDA and other required bodies in a timely manner or at all, agreements with acceptable terms may not be reached in a timely manner or at all with contract research organizations, to conduct the trials, a sufficient number of subjects may not be recruited and enrolled in the trials, and third-party manufacturers of the materials for use in the trials may encounter delays and problems in the manufacturing process, including failure to produce materials in sufficient quantities or of an acceptable quality to complete the trials. Clinical trial delays could shorten any periods during which our products have patent protection and may allow our competitors to bring products to market before we do, which could impair our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates and may harm our business and results of operations.
| 31 |
If we are not able to obtain any required regulatory approvals for ANEB-001, we will not be able to commercialize our lead drug candidate and our ability to generate revenue will be limited.
Our drug candidate is a treatment in development for ACI. We must successfully complete clinical trials for our drug candidate before we can apply for marketing approval. Even if we complete our clinical trials, it does not assure marketing approval. Our clinical trials may be unsuccessful, which would materially harm our business. Even if our initial clinical trials are successful, we are required to conduct additional clinical trials to establish our drug candidate’s safety and efficacy, before a NDA or BLA, or their foreign equivalents can be filed with the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities for marketing approval of our drug candidate.
Success in early phases of preclinical and clinical trials does not ensure that later clinical trials will be successful, and interim results of a clinical trial do not necessarily predict final results. A failure of one or more of our clinical trials can occur at any stage of testing. We may experience unforeseen events during, or as a result of, the clinical trial process that could delay or prevent our ability to receive regulatory approval or commercialize our drug candidate. The research, testing, manufacturing, labeling, packaging, storage, approval, sale, marketing, advertising and promotion, pricing, export, import and distribution of drug products are subject to extensive regulation by the FDA and other regulatory authorities in the United States and other countries, which regulations differ from country to country. We are not permitted to market our drug in the United States until we receive approval of an NDA from the FDA, or in any foreign countries until we receive the requisite approval from such countries. In the United States, the FDA generally requires the completion of clinical trials of each drug to establish its safety and efficacy and extensive pharmaceutical development to ensure its quality before an NDA is approved. Regulatory authorities in other jurisdictions impose similar requirements. Of the large number of drugs in development, only a small percentage result in the submission of an NDA to the FDA and even fewer are eventually approved for commercialization. If our development efforts for our drug candidate, including regulatory approval, are not successful for its planned indications, or if adequate demand for our drug candidate is not generated, our business will be materially adversely affected.
Our success depends on the receipt of regulatory approval and the issuance of such regulatory approvals is uncertain and subject to a number of risks, including the following:
| ● | the results of toxicology studies may not support the filing of an IND for our drug candidate or the FDA may require additional toxicology studies; | |
| ● | the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities or IRB may disagree with the design or implementation of our clinical trials; | |
| ● | it may be difficult to run clinical trials involving the administration of THC to subjects because THC is a controlled substance and is illegal in certain jurisdictions; | |
| ● | we may not be able to provide acceptable evidence of our drug candidate’s safety and efficacy; | |
| ● | the results of our clinical trials may not be satisfactory or may not meet the level of statistical or clinical significance required by the FDA or other regulatory agencies for marketing approval; | |
| ● | the dosing of our drug candidate in a particular clinical trial may not be at an optimal level; | |
| ● | patients in our clinical trials may suffer adverse effects for reasons that may or may not be related to our drug candidate; | |
| ● | the data collected from clinical trials may not be sufficient to support the submission of an NDA, BLA or other submission or to obtain regulatory approval in the United States or elsewhere; | |
| ● | the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may fail to approve the manufacturing processes or facilities of third-party manufacturers with which we contract for clinical and commercial supplies; and | |
| ● | the approval policies or regulations of the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may significantly change in a manner rendering our clinical data insufficient for approval. |
Failure to obtain regulatory approval for our drug candidate for the foregoing, or any other reasons, will prevent us from commercializing our drug candidate, and our ability to generate revenue will be materially impaired. We cannot guarantee that regulators will agree with our assessment of the results of the clinical trials we intend to conduct in the future or that such trials will be successful. The FDA and other regulators have substantial discretion in the approval process and may refuse to accept any application or may decide that our data is insufficient for approval and require additional clinical trials, or preclinical or other studies. In addition, varying interpretations of the data obtained from preclinical and clinical testing could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval of our drug candidate.
| 32 |
We have not submitted an NDA or received regulatory approval to market our drug candidate in any jurisdiction. We have only limited experience in filing the applications necessary to gain regulatory approvals and expect to rely on consultants and third party contract research organizations, with expertise in this area to assist us in this process. Securing regulatory approvals to market a product requires the submission of preclinical, clinical, and/or pharmacokinetic data, information about product manufacturing processes and inspection of facilities and supporting information to the appropriate regulatory authorities for each therapeutic indication to establish a drug candidate’s safety and efficacy for each indication. Our drug candidate may prove to have undesirable or unintended side effects, toxicities or other characteristics that may preclude us from obtaining regulatory approval or prevent or limit commercial use with respect to one or all intended indications.
The process of obtaining regulatory approvals is expensive, often takes many years, if approval is obtained at all, and can vary substantially based upon, among other things, the type, complexity and novelty of the drug candidate involved, the jurisdiction in which regulatory approval is sought and the substantial discretion of the regulatory authorities. Changes in regulatory approval policies during the development period, changes in or the enactment of additional statutes or regulations, or changes in regulatory review for a submitted product application may cause delays in the approval or rejection of an application.
Even if we receive regulatory approval for ANEB-001, our lead drug candidate, we may not be able to successfully commercialize the product and the revenue that we generate from its sales, if any, may be limited.
If approved for marketing, the commercial success of ANEB-001 will depend upon the product’s acceptance by the medical community, including physicians, patients and healthcare payors. The degree of market acceptance for our drug candidate will depend on a number of factors, including:
| ● | demonstration of clinical safety and efficacy; | |
| ● | relative convenience, dosing burden and ease of administration; | |
| ● | the prevalence and severity of any adverse effects; | |
| ● | the willingness of physicians to prescribe our drug candidate, and the target patient population to try new therapies; | |
| ● | efficacy of our drug candidate compared to competing products; | |
| ● | the introduction of any new products that may in the future become available targeting indications for which our drug candidate may be approved; | |
| ● | new procedures or therapies that may reduce the incidences of any of the indications in which our drug candidate may show utility; | |
| ● | pricing and cost-effectiveness; | |
| ● | the inclusion or omission of our drug candidate in applicable therapeutic and vaccine guidelines; | |
| ● | the effectiveness of our own or any future collaborators’ sales and marketing strategies; | |
| ● | limitations or warnings contained in approved labeling from regulatory authorities; | |
| ● | our ability to obtain and maintain sufficient third-party coverage or reimbursement from government healthcare programs, including Medicare and Medicaid, private health insurers and other third-party payors or to receive the necessary pricing approvals from government bodies regulating the pricing and usage of therapeutics; and | |
| ● | the willingness of patients to pay out-of-pocket in the absence of third-party coverage or reimbursement or government pricing approvals. |
If our drug candidate is approved, but does not achieve an adequate level of acceptance by physicians, healthcare payors and patients, we may not generate sufficient revenue and we may not be able to achieve or sustain profitability. Our efforts to educate the medical community and third-party payors on the benefits of our drug candidates may require significant resources and may never be successful.
| 33 |
In addition, even if we obtain regulatory approvals, the timing or scope of any approvals may prohibit or reduce our ability to commercialize our drug candidate successfully. For example, if the approval process takes too long, we may miss market opportunities and give other companies the ability to develop competing products or establish market dominance. Any regulatory approval we ultimately obtain may be limited or subject to restrictions or post-approval commitments that render our drug candidate not commercially viable. For example, regulatory authorities may approve our drug candidate for fewer or more limited indications than we request, may not approve the price we intend to charge for our drug candidate, may grant approval contingent on the performance of costly post-marketing clinical trials, or may approve our drug candidate with a label that does not include the labeling claims necessary or desirable for the successful commercialization of that indication. Further, the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may place conditions on approvals or require risk management plans or a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (“REMS”) to assure the safe use of the drug. If the FDA concludes a REMS is needed, the sponsor of the NDA must submit a proposed REMS; the FDA will not approve the NDA without an approved REMS, if required. A REMS could include medication guides, physician communication plans, or elements to assure safe use, such as restricted distribution methods, patient registries and other risk minimization tools. The FDA may also require a REMS for an approved product when new safety information emerges. Any of these limitations on approval or marketing could restrict the commercial promotion, distribution, prescription or dispensing of our drug candidate. Moreover, product approvals may be withdrawn for non-compliance with regulatory standards or if problems occur following the initial marketing of the product. Any of the foregoing scenarios could materially harm the commercial success of our drug candidate.
Even if we obtain marketing approval for ANEB-001, we will be subject to ongoing obligations and continued regulatory review, which may result in significant additional expense. Additionally, ANEB-001 could be subject to labeling and other restrictions and withdrawal from the market and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or if we experience unanticipated problems with ANEB-001.
Even if we obtain regulatory approval for ANEB-001 for an indication, the FDA or foreign equivalent may still impose significant restrictions on their indicated uses or marketing or the conditions of approval, or impose ongoing requirements for potentially costly and time-consuming post-approval studies and post-market surveillance to monitor safety and efficacy. Our drug candidate will also be subject to ongoing regulatory requirements governing the manufacturing, labeling, packaging, storage, distribution, safety surveillance, advertising, promotion, recordkeeping and reporting of adverse events and other post-market information. These requirements include registration with the FDA, as well as continued compliance with current GCP regulations, for any clinical trials that we conduct post-approval. In addition, manufacturers of drug products and their facilities are subject to continual review and periodic inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities for compliance with CGMP requirements relating to quality control, quality assurance and corresponding maintenance of records and documents.
The FDA has the authority to require a REMS as part of an NDA or after approval, which may impose further requirements or restrictions on the distribution or use of an approved drug, such as limiting prescribing to certain physicians or medical centers that have undergone specialized training, limiting treatment to patients who meet certain safe-use criteria or requiring patient testing, monitoring and/or enrollment in a registry.
With respect to sales and marketing activities by us or any future partner, advertising and promotional materials must comply with FDA rules in addition to other applicable federal, state and local laws in the United States and similar legal requirements in other countries. In the United States, the distribution of product samples to physicians must comply with the requirements of the U.S. Prescription Drug Marketing Act. Application holders must obtain FDA approval for product and manufacturing changes, depending on the nature of the change. We may also be subject, directly or indirectly through our customers and partners, to various fraud and abuse laws, including, without limitation, the U.S. Anti-Kickback Statute, U.S. False Claims Act, and similar state laws, which impact, among other things, our proposed sales, marketing, and scientific/educational grant programs. If we participate in the U.S. Medicaid Drug Rebate Program, the Federal Supply Schedule of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, or other government drug programs, we will be subject to complex laws and regulations regarding reporting and payment obligations. All of these activities are also potentially subject to U.S. federal and state consumer protection and unfair competition laws. Similar requirements exist in many of these areas in other countries.
If we or a regulatory agency discovers previously unknown problems with our product, such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, problems with the facility where the product is manufactured, or we or our manufacturers fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, we may be subject to the following administrative or judicial sanctions:
| ● | restrictions on the manufacturing or marketing of the product (including complete withdrawal or recall of the product); | |
| ● | warning letters or holds on post-approval clinical trials; | |
| ● | FDA’s refusal to approve pending NDA’s or supplements to approved NDA’s; | |
| ● | suspension or revocation of product license approvals; | |
| ● | product seizures or detentions; | |
| ● | FDA’s refusal to allow imports or exports of products; or | |
| ● | civil penalties, criminal penalties or injunctions. |
The occurrence of any event or penalty described above may inhibit our ability to commercialize our drug candidate and generate revenue. Adverse regulatory action, whether pre- or post-approval, can also potentially lead to product liability claims and increase our product liability exposure.
| 34 |
Current and future legislation may increase the difficulty and cost for us to obtain marketing approval of and commercialize ANEB-001 and affect the prices we may obtain.
In the United States and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the healthcare system that could prevent or delay marketing approval for our drug candidate, restrict or regulate post-approval activities and affect our ability to profitably sell ANEB-001. Legislative and regulatory proposals have been made to expand post-approval requirements and restrict sales and promotional activities for pharmaceutical products. We do not know whether additional legislative changes will be enacted, or whether the FDA regulations, guidance or interpretations will be changed, or what the impact of such changes on the marketing approvals of our drug candidate, if any, may be. In addition, increased scrutiny by the U.S. Congress of the FDA’s approval process may significantly delay or prevent marketing approval, as well as subject us to more stringent product labeling and post-marketing testing and other requirements.
In the United States, the Medicare Modernization Act (“MMA”) changed the way Medicare covers and pays for pharmaceutical products. The MMA expanded Medicare coverage for drug purchases by the elderly and introduced a new reimbursement methodology based on average sales prices for drugs. In addition, the MMA authorized Medicare Part D prescription drug plans to use formularies where they can limit the number of drugs that will be covered in any therapeutic class. As a result of this legislation and the expansion of federal coverage of drug products, we expect that there will be additional pressure to contain and reduce costs. These cost reduction initiatives and other provisions of this legislation could decrease the coverage and price that we receive for our drug candidate and could seriously harm our business. While the MMA applies only to drug benefits for Medicare beneficiaries, private payors often follow Medicare coverage policy and payment limitations in setting their own reimbursement rates, and any reduction in reimbursement that results from the MMA may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors.
The Affordable Care Act (“ACA”) was intended to broaden access to health insurance, reduce or constrain the growth of healthcare spending, enhance remedies against fraud and abuse, add new transparency requirements for healthcare and health insurance industries, impose new taxes and fees on the health industry and impose additional health policy reforms. The ACA revised the definition of “average manufacturer price” for reporting purposes, which could increase the amount of Medicaid drug rebates to states. Further, the law imposed a significant annual fee on companies that manufacture or import branded prescription drug products.
The ACA remains subject to legislative efforts to repeal, modify or delay the implementation of the law. Efforts to date have generally been unsuccessful. If the ACA is repealed or modified, or if implementation of certain aspects of the Health Care Reform Law are delayed, such repeal, modification or delay may materially adversely impact our business, strategies, prospects, operating results or financial condition. We are unable to predict the full impact of any repeal or modification in the implementation of the ACA on us at this time.
In addition, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted in the United States since the ACA was enacted. We expect that additional federal healthcare reform measures will be adopted in the future, any of which could limit the amounts that federal and state governments will pay for healthcare products and services, and in turn could significantly reduce the projected value of certain development projects and reduce or eliminate our profitability.
| 35 |
ANEB-001, our lead drug candidate, may face competition sooner than expected.
Our success will depend in part on our ability to obtain and maintain patent protection for important aspects of ANEB-001 and technologies and to prevent third parties from infringing upon our proprietary rights. We must also operate without infringing upon patents and proprietary rights of others, including by obtaining appropriate licenses to patents or other proprietary rights held by third parties, if necessary. However, the applications we have filed or may file in the future may never yield patents that protect our inventions and intellectual property assets. Failure to obtain patents that sufficiently cover our formulations and technologies would limit our protection against compounding pharmacies, outsourcing facilities, generic drug manufacturers, pharmaceutical companies and other parties who may seek to copy our products, produce products substantially similar to ours or use technologies substantially similar to those we own.
We will be completely dependent on third parties to manufacture ANEB-001, and our commercialization of ANEB-001 could be halted, delayed or made less profitable if those third parties fail to obtain manufacturing approval from the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities, fail to provide us with sufficient quantities of ANEB-001 or fail to do so at acceptable quality levels or prices.
We do not currently have, nor do we plan to acquire, the capability or infrastructure to manufacture the API in ANEB-001 for use in our clinical trials or for commercial product, if any. In addition, we do not have the capability to encapsulate our drug candidate as a finished drug product for commercial distribution. As a result, we will be obligated to rely on contract manufacturers, if and when our drug candidate is approved for commercialization. We have not entered into an agreement with any contract manufacturers for commercial supply and may not be able to engage a contract manufacturer for commercial supply of our drug candidate on favorable terms to us, or at all.
The facilities used by our contract manufacturers to manufacture our drug candidate must be approved by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities pursuant to inspections that will be conducted after we submit an NDA or BLA to the FDA or their equivalents to other relevant regulatory authorities. We will not control the manufacturing process of, and will be completely dependent on, our contract manufacturing partners for compliance with CGMP regulations for manufacture of both active drug substances and finished drug products. These CGMP regulations cover all aspects of the manufacturing, testing, quality control and record keeping relating to our drug candidates. If our contract manufacturers do not successfully manufacture material that conforms to our specifications and the strict regulatory requirements of the FDA or others, they will not be able to secure and/or maintain regulatory approval for their manufacturing facilities. If the FDA or a comparable foreign regulatory authority does not approve these facilities for the manufacture of our drug candidate or if it withdraws any such approval in the future, we may need to find alternative manufacturing facilities, which would significantly impact our ability to develop, obtain regulatory approval for or market our drug candidate, if approved.
Our contract manufacturers will be subject to ongoing periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and corresponding state and foreign agencies for compliance with CGMP regulations and similar regulatory requirements. We will not have control over our contract manufacturers’ compliance with these regulations and standards. Failure by any of our contract manufacturers to comply with applicable regulations could result in sanctions being imposed on us, including fines, injunctions, civil penalties, failure to grant approval to market our drug candidate, delays, suspensions or withdrawals of approvals, operating restrictions and criminal prosecutions, any of which could significantly and adversely affect our business. In addition, we will not have control over the ability of our contract manufacturers to maintain adequate quality control, quality assurance and qualified personnel. Failure by our contract manufacturers to comply with or maintain any of these standards could adversely affect our ability to develop, obtain regulatory approval for or market any of our drug candidate.
| 36 |
If, for any reason, these third parties are unable or unwilling to perform, we may not be able to terminate our agreements with them, and we may not be able to locate alternative manufacturers or formulators or enter into favorable agreements with them and we cannot be certain that any such third parties will have the manufacturing capacity to meet future requirements. If these manufacturers or any alternate manufacturer of finished drug product experiences any significant difficulties in its respective manufacturing processes for our API or finished products or should cease doing business with us, we could experience significant interruptions in the supply of our drug candidate or may not be able to create a supply of our drug candidate at all. Were we to encounter manufacturing issues, our ability to produce a sufficient supply of our drug candidate might be negatively affected. Our inability to coordinate the efforts of our third-party manufacturing partners, or the lack of capacity available at our third party manufacturing partners, could impair our ability to supply our drug candidate at required levels. Because of the significant regulatory requirements that we would need to satisfy in order to qualify a new bulk or finished product manufacturer, if we face these or other difficulties with our current manufacturing partners, we could experience significant interruptions in the supply of our drug candidate if we decided to transfer the manufacturing of our drug candidate to one or more alternative manufacturers in an effort to deal with the difficulties.
Any manufacturing problem or the loss of a contract manufacturer could be disruptive to our operations and result in lost sales. Additionally, we rely on third parties to supply the raw materials needed to manufacture our potential product. Any reliance on suppliers may involve several risks, including a potential inability to obtain critical materials and reduced control over production costs, delivery schedules, reliability and quality. Any unanticipated disruption to a future contract manufacturer caused by problems at suppliers could delay shipment of our drug candidate, increase our cost of goods sold and result in lost sales.
We cannot guarantee that our future manufacturing and supply partners will be able to reduce the costs of commercial scale manufacturing of our drug candidate over time. If the commercial-scale manufacturing costs of our drug candidate are higher than expected, these costs may significantly impact our operating results. In order to reduce costs, we may need to develop and implement process improvements. However, in order to do so, we will need, from time to time, to notify or make submissions with regulatory authorities, and the improvements may be subject to approval by such regulatory authorities.
We cannot be sure that we will receive these necessary approvals or that these approvals will be granted in a timely fashion. We also cannot guarantee that we will be able to enhance and optimize output in our commercial manufacturing process. If we cannot enhance and optimize output, we may not be able to reduce our costs over time.
| 37 |
Any termination or suspension of, or delays in the commencement or completion of, any necessary studies of ANEB-001, our lead drug candidate, for any indications could result in increased costs to us, delay or limit our ability to generate revenue and adversely affect our commercial prospects.
The commencement and completion of clinical studies can be delayed for a number of reasons, including delays related to:
| ● | the FDA or a comparable foreign regulatory authority failing to grant permission to proceed and placing the clinical study on hold; | |
| ● | subjects for clinical testing failing to enroll or remain in our trials at the rate we expect; | |
| ● | a facility manufacturing our drug candidate being ordered by the FDA or other government or regulatory authorities to temporarily or permanently shut down due to violations of CGMP requirements or other applicable requirements, or contamination of our drug candidate in the manufacturing process; | |
| ● | any changes to our manufacturing process that may be necessary or desired; | |
| ● | subjects choosing an alternative treatment for the indications for which we are developing our drug candidate, or participating in competing clinical studies; | |
| ● | subjects experiencing severe or unexpected drug-related adverse effects; | |
| ● | reports from clinical testing on similar technologies and products raising safety and/or efficacy concerns; | |
| ● | third-party clinical investigators losing their license or permits necessary to perform our clinical trials, not performing our clinical trials on our anticipated schedule or employing methods consistent with the clinical trial protocol, CGMP requirements, or other third parties not performing data collection and analysis in a timely or accurate manner; | |
| ● | inspections of clinical study sites by the FDA, comparable foreign regulatory authorities, or IRB’s finding regulatory violations that require us to undertake corrective action, result in suspension or termination of one or more sites or the imposition of a clinical hold on the entire study, or that prohibit us from using some or all of the data in support of our marketing applications with the FDA; | |
| ● | third-party contractors becoming debarred or suspended or otherwise penalized by the FDA or other government or regulatory authorities for violations of regulatory requirements, in which case we may need to find a substitute contractor, and we may not be able to use some or any of the data produced by such contractors in support of our marketing applications with the FDA; | |
| ● | one or more IRB’s refusing to approve, suspending or terminating the study at an investigational site, precluding enrollment of additional subjects, or withdrawing its approval of the trial; reaching agreement on acceptable terms with prospective contract research organizations and clinical trial sites, the terms of which can be subject to extensive negotiation and may vary significantly among different contract research organizations and trial sites; | |
| ● | deviations of the clinical sites from trial protocols or dropping out of a trial; | |
| ● | adding new clinical trial sites; | |
| ● | the inability of the contract research organization to execute any clinical trials for any reason; and | |
| ● | government or regulatory delays or “clinical holds” requiring suspension or termination of a trial. |
Product development costs for our drug candidate will increase if we have delays in testing or approval or if we need to perform more or larger clinical studies than planned. Additionally, changes in regulatory requirements and policies may occur and we may need to amend study protocols to reflect these changes. Amendments may require us to resubmit our study protocols to the FDA, comparable foreign regulatory authorities, and IRB’s for reexamination, which may impact the costs, timing or successful completion of that study. If we experience delays in completion of, or if we, the FDA or other regulatory authorities, the IRB, or other reviewing entities, or any of our clinical study sites suspend or terminate any of our clinical studies of our drug candidate, its commercial prospects may be materially harmed and our ability to generate product revenues will be delayed. Any delays in completing our clinical trials will increase our costs, slow down our development and approval process and jeopardize our ability to commence product sales and generate revenues. Any of these occurrences may harm our business, financial condition and prospects significantly. In addition, many of the factors that cause, or lead to, termination or suspension of, or a delay in the commencement or completion of, clinical studies may also ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our drug candidate. In addition, if one or more clinical studies are delayed, our competitors may be able to bring products to market before we do, and the commercial viability of our drug candidate could be significantly reduced.
Clinical drug development involves a lengthy and expensive process with an uncertain outcome, and results of earlier studies and trials may not be predictive of future trial results.
Clinical testing of our drug candidate is expensive and can take many years to complete, and its outcome is inherently uncertain. Failure can occur at any time during the clinical trial process. The results of preclinical testing and early clinical trials may not be predictive of the results of later-stage clinical trials. We cannot assure you that the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities will view the results as we do or that any future trials of our drug candidate will achieve positive results. Drugs in later stages of clinical trials may fail to show the desired safety and efficacy traits despite having progressed through preclinical testing and initial clinical trials. A number of companies in the biopharmaceutical industry have suffered significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials due to lack of efficacy or adverse safety profiles, notwithstanding promising results in earlier trials. Any future clinical trial results for our drug candidate may not be successful.
In addition, a number of factors could contribute to a lack of favorable safety and efficacy results for our drug candidate. For example, such trials could result in increased variability due to varying site characteristics, such as local standards of care and differences in evaluation period, and due to varying patient characteristics including demographic factors and health status.
| 38 |
ANEB-001, our lead product candidate, may have undesirable side effects which may delay or prevent marketing approval, or, if approval is received, require it to be taken off the market, require it to include safety warnings or otherwise limit sales of the product.
Unforeseen side effects from ANEB-001 could arise either during clinical development or, if approved, after the product has been marketed. This could cause regulatory approvals for, or market acceptance of, the product to be harder and more costly to obtain.
To date, no serious adverse events have been attributed to ANEB-001. The results of our planned or any future clinical trials may show that our product candidate causes undesirable or unacceptable side effects, which could interrupt, delay or halt clinical trials, and result in delay of, or failure to obtain, marketing approval from the FDA and other regulatory authorities, or result in marketing approval from the FDA and other regulatory authorities with restrictive label warnings. If our product candidate receives marketing approval and we or others later identify undesirable or unacceptable side effects caused by the use of our product:
| ● | regulatory authorities may withdraw their approval of the product, which would force us to remove the product from the market; | |
| ● | regulatory authorities may require the addition of labeling statements, specific warnings, a contraindication, or field alerts to physicians, pharmacies and others; | |
| ● | we may be required to change instructions regarding the way the product is administered, conduct additional clinical trials or change the labeling of the product; | |
| ● | we may be subject to limitations on how we may promote the product; | |
| ● | sales of the product may decrease significantly; | |
| ● | we may be subject to litigation or product liability claims; and | |
| ● | our reputation may suffer. |
Any of these events could prevent us or our potential future collaborators from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of the product or could substantially increase commercialization costs and expenses, which in turn could delay or prevent us from generating significant revenues from the sale of our product.
| 39 |
Risks Related to Government Regulation of our Industry
Legislative or regulatory reform of the healthcare system may affect our ability to sell our products profitably.
In both the U.S. and certain foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory proposals to change the healthcare system in ways that could impact our ability to sell future products and profitability. On March 23, 2010, President Obama signed into law the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act (collectively, “PPACA”), which includes a number of healthcare reform provisions and requires most U.S. citizens to have health insurance. The law, among other things, imposes a significant annual fee on companies that manufacture or import branded prescription drug products, addresses a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for drugs that are inhaled, infused, instilled, implanted or injected, increases the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and extends the rebate program to individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations, and establishes a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50% point-of-sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs to be covered under Medicare Part D. Substantial new provisions affecting compliance also have been added, which may require modification of business practices with healthcare practitioners.
In the coming years, additional changes could be made to governmental healthcare programs that could significantly impact the development and success of our future product candidates, and we could be adversely affected by current and future healthcare reforms.
Clinical trials for ANEB-001 have and may in the future be conducted outside the United States and not under an IND, and where this is the case, the FDA may not accept data from such trials.
Although the FDA may accept data from clinical trials conducted outside the United States and not under an IND in support of research or marketing applications for our product candidates, this is subject to certain conditions set out in 21 C.F.R. § 312.120. For example, such foreign clinical trials should be conducted in accordance with GCP, including review and approval by an independent ethics committee and obtaining the informed consent from subjects of the clinical trials. The FDA must also be able to validate the data from the study through an onsite inspection if the agency deems it necessary. The foreign clinical data should also be applicable to the U.S. population and U.S. medical practice. Other factors that may affect the acceptance of foreign clinical data include differences in clinical conditions, study populations or regulatory requirements between the U.S. and the foreign country.
| 40 |
Risks Related to Ownership of Our Common Stock
We are an “emerging growth company” and our election to delay adoption of new or revised accounting standards applicable to public companies may result in our financial statements not being comparable to those of some other public companies. As a result of this and other reduced disclosure requirements applicable to emerging growth companies, our securities may be less attractive to new investors.
As a company with less than $1.07 billion in annual revenue, we qualify as an “emerging growth company” under the Jumpstart our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”). An emerging growth company may take advantage of specified reduced reporting requirements that are otherwise generally applicable to public companies. In particular, as an emerging growth company we:
| ● | are not required to obtain an attestation and report from our auditors on our management’s assessment of our internal control over financial reporting pursuant to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act; | |
| ● | are not required to provide a detailed narrative disclosure discussing our compensation principles, objectives and elements and analyzing how those elements fit with our principles and objectives (commonly referred to as “compensation discussion and analysis”); | |
| ● | are not required to obtain a non-binding advisory vote from our stockholders on executive compensation or golden parachute arrangements (commonly referred to as the “say-on-pay,” “say-on-frequency” and “say-on-golden-parachute” votes); | |
| ● | are exempt from certain executive compensation disclosure provisions requiring a pay-for-performance graph and CEO pay ratio disclosure; | |
| ● | may present only two years of audited financial statements and only two years of related Management’s Discussion & Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (“MD&A”); and | |
| ● | are eligible to claim longer phase-in periods for the adoption of new or revised financial accounting standards under §107 of the JOBS Act. |
We intend to take advantage of all of these reduced reporting requirements and exemptions, including the longer phase-in periods for the adoption of new or revised financial accounting standards under §107 of the JOBS Act. Our election to use the phase-in periods may make it difficult to compare our financial statements to those of non-emerging growth companies and other emerging growth companies that have opted out of the phase-in periods under §107 of the JOBS Act.
Certain of these reduced reporting requirements and exemptions were already available to us due to the fact that we also qualify as a “smaller reporting company” under SEC rules. For instance, smaller reporting companies are not required to obtain an auditor attestation and report regarding management’s assessment of internal control over financial reporting, are not required to provide a compensation discussion and analysis, are not required to provide a pay-for-performance graph or CEO pay ratio disclosure, and may present only two years of audited financial statements and related MD&A disclosure.
Under the JOBS Act, we may take advantage of the above-described reduced reporting requirements and exemptions for up to five years after our initial sale of common equity pursuant to a registration statement declared effective under the Securities Act, or such earlier time that we no longer meet the definition of an emerging growth company. In this regard, the JOBS Act provides that we would cease to be an “emerging growth company” if we have more than $1.07 billion in annual revenue, have more than $700 million in market value of our common stock held by non-affiliates, or issue more than $1 billion in principal amount of non-convertible debt over a three-year period. Under current SEC rules, however, we will continue to qualify as a “smaller reporting company” for so long as we have a public float (i.e., the market value of common equity held by non-affiliates) of less than $250 million as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter. We cannot predict if new investors will find our securities less attractive due to our reliance on these exemptions.
The trading price and volume of our common stock in the public markets has experienced, and may in the future experience, volatility due to a variety of factors, many of which are beyond our control.
Since our common stock started trading on The Nasdaq Capital Market, it has been relatively thinly traded and at times been subject to price volatility. From May 10, 2021 to September 14, 2021, the price of our common stock ranged from a low of $6.31 on May 14, 2021 to a high of $9.33 on May 21, 2021, with an average daily trading volume of 16,626 shares. The market price of our common stock may fluctuate substantially as a result of many factors, some of which are beyond our control. These fluctuations could cause you to lose all or part of the value of your investment in our common stock. Factors that could cause fluctuations in the market price of our common stock include the following:
| ● | quarterly variations in our results of operations; | |
| ● | results of operations that vary from the expectations of securities analysts and investors; | |
| ● | results of operations that vary from those of our competitors; | |
| ● | changes in expectations as to our future financial performance, including financial estimates by securities analysts; | |
| ● | publication of research reports about us or the pharmaceutical industry; | |
| ● | announcements by us or our competitors of significant contracts, acquisitions or capital commitments; | |
| ● | announcements by third parties of significant claims or proceedings against us; | |
| ● | changes affecting the availability of financing in the wholesale and consumer lending markets; | |
| ● | regulatory developments in the pharmaceutical industry; | |
| ● | significant future sales of our common stock, and additions or departures of key personnel; | |
| ● | the realization of any of the other risk factors presented in this prospectus; and | |
| ● | general economic, market and currency factors and conditions unrelated to our performance. |
| 41 |
In addition, the stock market in general has experienced significant price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to operating performance of individual companies. These broad market factors may seriously harm the market price of our common stock, regardless of our operating performance. In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation has often been instituted. A class action suit against us could result in significant liabilities and, regardless of the outcome, could result in substantial costs and the diversion of our management’s attention and resources.
We are incurring significantly increased costs as a result of operating as a public company, and our management is required to devote substantial time to compliance efforts.
As a public company, we are incurring significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. For example, we are subject to the reporting requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), the accounting and internal controls provisions of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, as amended, and will be required to comply with the applicable requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 (the “Dodd-Frank Act”), as well as rules and regulations subsequently implemented by the SEC and Nasdaq, including the establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and changes in corporate governance practices. Our management and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount of time and resources to complying with these requirements. Moreover, these rules and regulations are increasing our legal and financial compliance costs and will make some activities more time-consuming and costly. In particular, we expect to incur significant expenses and devote substantial management effort toward ensuring compliance with the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which will increase when we are no longer an “emerging growth company,” as defined by the JOBS Act. These new obligations will require substantial attention from our management team and could divert their attention away from the day-to-day management of our business. We will need to hire additional accounting and financial staff with appropriate public company experience and technical accounting knowledge and maintain an internal audit function. We cannot predict or estimate the amount of additional costs we may incur as a result of being a public company or the timing of such costs. These rules and regulations could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our board of directors and board committees or as executive officers, and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
We manage our business operations from our principal executive office in Lakeway, Texas, in 700 square feet of leased space under a sublease with JFL Capital Management LLC, a company controlled by Joseph F. Lawler, the founder and a director of our Company. Our office lease is month-to-month, and currently we pay rent of approximately $1,200 per month. We believe our present office space is adequate for our current operations and for near-term planned expansion.
| 42 |
From time to time, we may be a party to litigation or subject to claims incident to the ordinary course of business. Although the results of litigation and claims cannot be predicted with certainty, we currently believe that the final outcome of these ordinary course matters will not have a material adverse effect on our business. Regardless of the outcome, litigation can have an adverse impact on us because of defense and settlement costs, diversion of management resources and other factors. We are not currently a party to any material legal proceedings, and our management believes that there are currently no claims or actions pending against us, the ultimate disposition of which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations or financial condition.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market Information
Our common stock has been publicly traded on The Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “ANEB” since May 7, 2021. Prior to that time, there was no public market for our common stock.
Holders of Record
As of September 15, 2021, there were approximately 5 holders of record of our common stock. This number does not include beneficial owners whose shares are held by nominees in street name.
Dividends
We have not declared or paid any cash dividends on our capital stock since our inception. We intend to retain future earnings, if any, to finance the operation and expansion of our business and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends to holders of common stock in the near-term future. Any future determination to declare cash dividends will be made at the discretion of our board of directors, subject to applicable laws, will depend on a number of factors, including our financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements, contractual restrictions, general business conditions, and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
The information required by Item 5 of Form 10-K regarding equity compensation plans is incorporated herein by reference to Item 12 of Part III of this Annual Report.
Unregistered sales of equity securities
On June 18, 2020, we issued 2,047,500 shares of Series A convertible preferred stock to 22NW, LP, an institutional accredited investor affiliated with Aron R. English, who became a director of the Company at such time, for aggregate net consideration of $3.0 million. No underwriters were used and the sale of these securities were made in reliance upon the exemption from registration provided by Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act for transactions by an issuer not involving a public offering. Each share of preferred stock automatically converted into shares of our common stock upon the closing of our IPO of our common stock in May 2021.
| 43 |
From July 1, 2020 through May 6, 2021, the date our registration statement on Form S-1 was declared effective (Reg. No. 333-254979), we granted to our directors, officers, employees and consultants options to purchase an aggregate of 604,404 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $2.18 per share, as well as 982,500 shares of restricted common stock. We deemed the equity grants and exercises of stock options issued under our equity compensation plans prior to the completion of our initial public offering in May 2021 to be exempt from registration in reliance on Rule 701 of the Securities Act as offers and sales of securities under compensatory benefit plans and contracts relating to compensation. Each of the recipients of securities in any transaction exempt from registration either received or had adequate access, through employment, business or other relationships, to information about us.
Use of Proceeds from Initial Public Offering
On May 11, 2021, we closed our IPO in which we issued and sold 3,078,224 shares of our common stock, including 78,224 shares pursuant to the underwriters’ exercise of their option to purchase additional shares, at a public offering price to the public of $7.00 per share, for aggregate gross proceeds of $21.5 million. All shares issued and sold in the initial public offering were registered under the Securities Act pursuant to a Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-254979), which was declared effective by the SEC on May 6, 2021. We received aggregate net proceeds from our initial public offering of approximately $19.8 million, after deducting a total of $1.8 million for underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by us. None of the underwriting discounts and commissions or offering expenses were incurred or paid to directors or officers of ours, or any of their associates, or to persons owning 10% or more of our common stock or to any affiliates of ours.
We have not used any of the net proceeds from the IPO to make payments, directly or indirectly, to any director or officer of ours, or any of their associates, to any person owning 10% or more of our common stock or to any affiliate of ours. There has been no material change in our planned use of the net proceeds from the IPO as described in our final prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b)(4) under the Securities Act with the SEC on May 10, 2021.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
None.
Item 6. Selected financial data
Not applicable.
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read together with our financial statements and related notes and other financial information appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Some of the information contained in this discussion and analysis includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. As a result of many factors, including those factors set forth in the “Risk Factors” section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, our actual results could differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion and analysis.
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biotechnology company developing novel solutions for people suffering from ACI and substance addiction. Our lead product candidate, ANEB-001, is intended to reverse the negative effects of ACI within 1 hour of administration. The signs and symptoms of ACI range from profound sedation to anxiety and panic to psychosis with hallucinations. There is no approved medical treatment currently available to specifically alleviate the symptoms of ACI. If approved by the FDA, we believe ANEB-001 has the potential to be the first FDA approved treatment of its kind on the market for reversing the effects of THC, the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis. Clinical trials completed to date have shown that ANEB-001 is rapidly absorbed, well tolerated and leads to weight loss, an effect that is consistent with central CB1 antagonism. We intend to launch a Phase 2 proof-of-concept trial for ANEB-001 in the fourth calendar quarter of 2021.
| 44 |
ACI episodes have become a widespread health issue in the United States, particularly in the increasing number of states that have legalized cannabis for personal and recreational use. The ingestion of large quantities of THC is a major cause of ACI. Excessive ingestion of THC via edible products such as candies and brownies, and intoxication from synthetic cannabinoids (also known as “synthetics,” “K2” or “spice”), are two leading causes of THC-related emergency room visits. Synthetic cannabinoids are analogous to fentanyl for opioids insofar as they are more potent at the cannabinoid receptor than their natural product congener THC. In recent years, hospital emergency rooms across the United States have seen a dramatic increase in patient visits with cannabis-related conditions. Before the legalization of cannabis, an estimated 450,000 patients visited hospital emergency rooms annually for cannabis-related conditions. In 2014, this number more than doubled to an estimated 1.1 million patients, according to data published in “Trends and Related Factors of Cannabis-Associated Emergency Department Visits in the United States: 2006-2014,” Journal of Addiction Medicine (May/June 2019), which provided a national estimate analyzing data from NEDS, the largest database of U.S. hospital-owned emergency department visits. Based on our own analysis of the most recent NEDS data, we believe that the number of hospitalizations grew to 1.74 million patients in 2018 and was growing at an approximately 15% compounded annual growth rate between 2012 and 2018. We believe the number of cannabis-related hospitalizations and other health problems associated with ACIs such as depression, anxiety and mental disorders will continue to increase substantially as more states pass laws legalizing cannabis for medical and recreational use. Given the consequences, there is an urgent need for a treatment to rapidly reverse the symptoms of ACI.
In May 2020, we entered into the royalty-bearing License Agreement with Vernalis to exploit its license compounds and licensed products to combat symptoms of ACI and substance addiction. We are currently developing our lead product candidate, ANEB-001 to quickly, and effectively, combat symptoms of ACI.
Our objective is to develop and commercialize new treatment options for patients suffering from ACI and addiction. Our lead product candidate is ANEB-001, a potent, small molecule cannabinoid receptor antagonist, to address the unmet medical need for a specific antidote for ACI. ANEB-001 is an orally bioavailable, rapidly absorbed treatment that we anticipate will reverse the symptoms of ACIs, in most cases within 1 hour of administration. Our proprietary position in the treatment of ACI is protected by rights to two patent applications covering various methods of use of the compound and delivery systems. We anticipate starting a Phase 2 proof-of-concept trial for ANEB-001 in the fourth calendar quarter of 2021.
We were incorporated in Delaware on April 23, 2020, and commenced operations in May 2020. Our operations to date have consisted of organizing and acquiring the license rights to Vernalis’ licensed products, assembling an executive team, starting preparations for a Phase 2 proof-of-concept trial, including the synthesis of a new active pharmaceutical ingredient, the development and filing of a clinical trial protocol with regulatory agencies in Europe and raising capital. Prior to our IPO, we funded our operations through a private placement of our series A convertible preferred stock and issuance of two promissory notes to a related party.
Recent Developments
On September 10, 2021, we completed finished product manufacturing of our lead drug ANEB-001 for use in our upcoming Phase 2 clinical study. In compliance with all current Good Manufacturing Practice requirements, ANEB-001’s active pharmaceutical ingredient was delivered to its contract manufacturer and filled into 10mg and 50mg capsules for finished product. We are on track to commence our Phase 2 proof-of-concept study in October 2021, which is ahead of schedule, and we expect initial topline results from the first cohort in the first half of calendar 2022.
Stock Split and Initial Public Offering
On April 23, 2021, we effected a six-for-one stock split of our common stock to be consummated prior to the completion of our IPO. All shares, stock options, warrants and per share information presented in the accompanying financial statements and notes thereto have been adjusted to reflect the stock split on a retroactive basis for all periods presented. There was no change in the par value of our common stock.
On May 11, 2021, we completed our IPO of 3,078,224 shares of our common stock, including the partial exercise by the underwriter of their option to purchase 78,224 additional shares of common stock, for aggregate gross proceeds of approximately $21,548,000 and our shares commenced trading on The Nasdaq Capital Market under the ticker symbol “ANEB.” We received approximately $19,783,000 in net proceeds after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and other offering expenses paid by us. Upon the closing of the IPO, a cashless exercise of Series A Preferred milestone warrants (“Milestone Warrants”) resulted in the issuance of 5,236,343 shares of Series A convertible preferred stock and all of the outstanding shares of Series A convertible preferred stock automatically converted into 7,283,843 shares of common stock.
| 45 |
Components of Results of Operations
Revenue
We have not generated any revenue since inception. If our development efforts for our current lead product candidate, ANEB-001, or other additional product candidates that we may develop in the future, are successful and result in marketing approval, or if we enter into collaboration or license agreements with third parties, we may generate revenue in the future from a combination of product sales or payments from such collaboration or license agreements. We cannot predict if, when, or to what extent we will generate revenue from the commercialization and sale of our product candidates. We have incurred operating losses since inception and expect to continue to incur significant operating losses and negative cash flows from operations in the future.
Research and Development Expenses
We expect to continue incurring significant research and development costs related to ANEB-001. Our research and development expenses for the year ended June 30, 2021 and for the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020 included research and development consulting expenses and costs associated with development of our lead product candidate, ANEB-001.
We anticipate that our research and development activities will account for a significant portion of our operating expenses and these costs are expensed as incurred. We expect to significantly increase our research and development efforts as we continue to develop ANEB-001 and conduct clinical trials with patients suffering from symptoms of ACI, as well as continue to expand our product-candidate pipeline. Research and development expenses include:
| ● | employee-related expenses, such as salaries, share-based compensation, benefits and travel expense for research and development personnel that we plan to hire; | |
| ● | direct third-party costs such as expenses incurred under agreements with CROs and CMOs; | |
| ● | costs associated with research and development activities of consultants; | |
| ● | manufacturing costs in connection with producing materials for use in conducting preclinical studies and clinical trials; | |
| ● | other third-party expenses directly attributable to the development of our product candidates; and | |
| ● | amortization expense for future asset purchases used in research and development activities. |
We currently have one lead product candidate; therefore, we do not track our internal research and development expenses on an indication-by-indication basis.
Research and development activities will continue to be central to our business model. We expect our research and development expenses to be significant over the next several years as we advance our current clinical development program and prepare to seek regulatory approval.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses for the year ended June 30, 2021 and for the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020 consisted primarily of professional fees, stock-based compensation, insurance, personnel costs and rent.
| 46 |
Fair Value Adjustment for Milestone Warrants
The Milestone Warrants are freestanding financial instruments that qualified as liabilities required to be recorded at fair value at the inception date and remeasured each reporting period until settlement or until the underlying shares are converted to common, with gains and losses arising from changes in fair value recognized in the statements of operations.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the Year Ended June 30, 2021 and For the Period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020
The following table summarizes our results of operations:
| For the Year ended | For the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to | |||||||||||
| June 30, 2021 | June 30, 2020 | Change | ||||||||||
| Research and development | $ | 2,269,998 | $ | 150,000 | $ | 2,119,998 | ||||||
| General and administrative | 1,343,755 | 23,351 | 1,320,404 | |||||||||
| Total operating expenses | 3,613,753 | 173,351 | 3,440,402 | |||||||||
| Loss from operations | (3,613,753 | ) | (173,351 | ) | (3,440,402 | ) | ||||||
| Other (income) expenses: | ||||||||||||
| Interest income | (1,020 | ) | - | (1,020 | ) | |||||||
| Interest expense | 11,767 | 1,286 | 10,481 | |||||||||
| Fair value adjustment for Milestone Warrants | 26,626,710 | - | 26,626,710 | |||||||||
| Other | 1,344 | - | 1,344 | |||||||||
| Total other expenses, net | 26,638,801 | 1,286 | 26,637,515 | |||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (30,252,554 | ) | $ | (174,637 | ) | $ | (30,077,917 | ) | |||
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses consisted of the following:
| For the Year ended | For the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to | |||||||||||
| June 30, 2021 | June 30, 2020 | Change | ||||||||||
| Pre-clinical and clinical studies | $ | 772,683 | $ | - | $ | 772,683 | ||||||
| Compensation and related benefits | 24,453 | - | 24,453 | |||||||||
| Stock compensation expense | 12,598 | - | 12,598 | |||||||||
| Other research and development | 1,460,264 | 150,000 | 1,310,264 | |||||||||
| Total research and development expenses | $ | 2,269,998 | $ | 150,000 | $ | 2,119,998 | ||||||
Other research and development for the year ended June 30, 2021 included $1,350,000 related to milestone payments made to Vernalis in the form of 192,857 shares of common stock issued from the IPO. For the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020, other research and development consisted of the $150,000 upfront license fee paid to Vernalis.
| 47 |
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consisted of the following:
| For the Year ended | For the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to | |||||||||||
| June 30, 2021 | June 30, 2020 | Change | ||||||||||
| Compensation and related benefits | $ | 164,359 | $ | - | $ | 164,359 | ||||||
| Professional and consultant fees | 572,760 | 23,351 | 549,409 | |||||||||
| Stock compensation expense | 187,349 | - | 187,349 | |||||||||
| Facilities, fees and other related costs | 419,287 | - | 419,287 | |||||||||
| Total general and administrative expenses | $ | 1,343,755 | $ | 23,351 | $ | 1,320,404 | ||||||
Interest Expense
Interest expense of $11,767 for the year ended June 30, 2021 was related to two promissory notes issued to a related party in May and June of 2020. The notes were repaid in March 2021.
Fair Value Adjustment for Milestone Warrants
As a result of changes in fair value, we recognized a charge of approximately $26,627,000 related to the Milestone Warrants for the year ended June 30, 2021.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
Since our inception in April 2020, we have incurred significant operating losses. We expect to incur significant expenses and operating losses in the future as we advance the clinical development of our programs. In May 2021, we completed our IPO in which we sold 3,078,224 shares of our common stock, including the exercise by the underwriter of their option to purchase 78,224 additional shares of common stock, at a public offering price of $7.00 per share. We received net proceeds from our IPO of approximately $19,783,000, after deducting underwriter discounts and offering expenses paid by us. As of June 30, 2021, we have cash of approximately $19,986,000.
We expect our current cash resources will be sufficient to operate into the first calendar quarter of 2023. We anticipate that additional capital will be needed to commence and complete a Phase 3 study of our drug candidate ANEB-001. As and if necessary, we will seek to raise these additional funds through various potential sources, such as equity and debt financings or through corporate collaboration and license agreements. We can give no assurances that we will be able to secure such additional sources of funds to support our operations, or, if such funds are available to us, that such additional financing will be sufficient to meet our needs.
Cash Flows
The following table sets forth a summary of our cash flows:
| For the Year ended | For the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to | |||||||
| June 30, 2021 | June 30, 2020 | |||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | $ | (4,871,189 | ) | $ | (150,772 | ) | ||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 21,831,854 | 3,175,752 | ||||||
| Net increase in cash | $ | 16,960,665 | $ | 3,024,980 | ||||
| 48 |
Operating Activities
During the year ended June 30, 2021, our operating activities used $4,871,189 in cash, which was less than the net loss of $30,252,554, primarily due to fair value adjustment for Milestone Warrants, stock-based compensation, increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses. These changes were partially offset by the increase in prepaid expenses and other current assets.
For the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020, our operating activities used $150,772 in cash, which was less than the net loss of $174,637, primarily due to an increase in accrued expenses.
Financing Activities
During the year ended June 30, 2021, cash provided by financing activities was $21,831,854. This was primarily due to proceeds received from the IPO and issuance of Milestone Warrants of $2,250,000 offset by the repayment of the related party promissory notes of approximately $200,000.
For the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020, cash provided by financing activities was $3,175,752. This was primarily due to proceeds from issuance of Series A convertible preferred stock and from issuance of promissory notes to related party.
Funding Requirements
We expect that our cash at June 30, 2021 will enable us to fund our current and planned operating expenses and capital expenditures for at least the next 12 months from the filing of this report. We have based these estimates on assumptions that may prove to be imprecise, and we may exhaust our available capital resources sooner that we currently expect. Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with the development of our programs, we are unable to estimate the amounts of increased capital outlays and operating expenses associated with completing the research and development of our product candidates.
Until such time, if ever, as we can generate substantial product revenue from sales of any of our current or future product candidates, we expect to finance our cash needs through a combination of equity offerings, debt financings and potential collaboration, license or development agreements. Debt financing and preferred equity financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures, or declaring dividends.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
License Agreement with Vernalis Development Limited
On May 26, 2020, we entered into an exclusive License Agreement with Vernalis. Pursuant to the License Agreement, Vernalis granted us an exclusive worldwide royalty-bearing license to develop and commercialize a compound that we refer to as ANEB-001, as well as access to and a right of reference with respect to any regulatory materials under its control. The License Agreement allows us to sublicense the rights thereunder to any person with similar or greater financial resources and expertise without Vernalis’ prior consent, provided the proposed sublicensee is not developing or commercializing a product that contains a CB1 antagonist or is for the same indication covered by the trials or market authorization for ANEB-001. In exchange for the exclusive license, we agreed to pay Vernalis a non-refundable signature fee of $150,000, total potential developmental milestone payments of up to $29,900,000, total potential sales milestone payments of up to $35,000,000, and low to mid-single digit royalties on net sales. Subsequently, in May 2021 as part of the IPO, we issued 192,857 shares of common stock to Vernalis in lieu of future milestone payments of $1,350,000.
| 49 |
Under the License Agreement, we purchased the API for ANEB-001 from Vernalis on an “as is” basis for $20,000. We have the sole discretion to carry out the development and commercialization of ANEB-001, including obtaining regulatory approvals, and we are responsible for all costs and expenses in connection therewith. We have access to certain regulatory materials, including study reports from clinical and non-clinical trials, under Vernalis’ control. We agreed to use commercially reasonable efforts to (i) develop and commercialize ANEB-001 in the United States and certain European countries and (ii) conduct a Phase 2 and human clinical trial within specified periods, which periods could be extended for a nominal fee. We also agreed to provide Vernalis with periodic reports of our activities and notice of market authorization within specified timeframes.
Office Lease, Manufacturing Contract and CRO Contract
We manage our business operations from our principal executive office in Lakeway, Texas, in 700 square feet of leased space under a sublease with a related party. Our office lease is month-to-month, and currently we pay rent of approximately $1,200 per month. In October 2020, we entered into an agreement with a third-party contract manufacturing organization. The total cost for the manufacturing contracts is approximately $973,000. Subsequently in February 2021, we entered into an agreement with a third-party CRO to manage and conduct our Phase 2 clinical trial in the fourth calendar quarter of 2021 with the anticipation of completing the trial by the first calendar quarter of 2022. The total cost for the CRO agreement is approximately €1,450,758 or $1,760,000.
We enter into contracts in the normal course of business with clinical trial sites and clinical supply manufacturers and other services and products for operating purposes. These contracts generally provide for termination after a notice period, and therefore, are cancellable contracts.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
Our financial statements are prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“U.S. GAAP”). The preparation of our financial statements and related disclosures requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, costs and expenses, and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities in our financial statements. We base our estimates on historical experience, known trends and events and various other factors that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. We evaluate our estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis. Our actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
While our significant accounting policies are described in more detail in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, to our financial statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we believe that the following accounting policies are those most critical to the judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our financial statements.
Accrued Research and Development Expenses
As part of the process of preparing our financial statements, we are required to estimate our accrued research and development expenses. This process involves reviewing open contracts and purchase orders, communicating with our personnel to identify services that have been performed on our behalf and estimating the level of service performed and the associated costs incurred for the services when we have not yet been invoiced or otherwise notified of the actual costs. The majority of our service providers invoice us in arrears for services performed and some require advanced payments. We make estimates of our accrued expenses of each balance sheet date in our financial statements based on facts and circumstances known to us at that time. Examples of estimated accrued research and development expenses include fees paid to:
| ● | CROs in connection with performing research services on our behalf and any clinical trials; | |
| ● | Investigative sites or other providers in connection with studies and any clinical trials; | |
| ● | Vendors in connection with the preparation of our NDA file, market and patient awareness programs, market research and analysis and medical education; and | |
| ● | Vendors related to product manufacturing, development and distribution of clinical supplies. |
| 50 |
We base our expenses for services rendered on our estimates of the services received and efforts expended pursuant to quotes, contracts and communicating with our vendors. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation, vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payments. There may be instances in which payments made to our vendors will exceed the level of services provided and result in a prepayment of the expense. In accruing service fees, we estimate the time period over which services will be performed and the level of effort to be expended in each period. If the actual timing of the performance of services or the level of effort varies from our estimate, we adjust the accrual or amount of prepaid or accrued expenses accordingly. Although we do not expect our estimates to be materially different from amounts actually incurred, our understanding of the status and timing of services performed relative to the actual status and timing of services performed may vary and may result in us reporting amounts that are too high or too low in any particular period.
Valuation of Milestone Warrants
We classified the Milestone Warrants as liabilities on our balance sheet as we determined they met the definition of a freestanding financial instrument since they are legally detachable. We remeasured the liabilities associated with Milestone Warrants to fair value at each reporting date, and immediately prior to exercise, and recognized changes in the fair value of the liabilities in our statements of operations recorded as “fair value adjustment for Milestone Warrants.” The Milestone Warrants were originated and exercised within the fiscal year, so they do not actually appear on the June 30, 2021 and 2020 balance sheets presented in the financial statements.
The fair value of the Milestone Warrant liability was determined using the Black Scholes option-pricing model utilizing inputs such as the fair value of the underlying stock, expected term, expected volatility of the underlying stock over the expected term, and the risk-free interest rate over the expected term. Changes to these assumptions could have a significant impact on the fair value of the Milestone Warrant liabilities and related fair value adjustments.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
In June 2020, the board of directors adopted the 2020 Stock Incentive Plan, which provided for the grant of qualified incentive stock options and nonqualified stock options or other awards to our employees, officers, directors, advisors, and outside consultants for the purchase of up to 1,650,000 shares of our common stock. Other awards include restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock appreciation rights and other stock-based awards. Other stock-based awards are awards valued in whole or in part by reference to, or are otherwise based on, shares of common stock. Stock options generally vest over a four-year period, at achievement of a performance requirement, or upon change of control (as defined in the applicable plan). The awards expire five years from the date of grant.
For the year ended June 30, 2021, we recorded stock-based compensation expense of $187,349 in general and administrative expenses and $12,598 in research and development expenses. No stock-based compensation expense was recognized for the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020.
We estimate the fair value of each stock option grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which uses inputs such as the fair value of our common stock, assumptions we make for the volatility of our common stock the expected term of the stock options, the risk-free interest rate for a period that approximates the expected term, and our expected dividend yield. The fair value of our common stock is used to determine the fair value of restricted stock.
Prior to our IPO, the fair value of our common stock was estimated on each grant date by our board of directors. In order to determine the fair value of our common stock, our board of directors considered, among other things, timely valuations of our common stock prepared by an unrelated third-party valuation firm in accordance with the guidance provided by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants Practice Guide, Valuation of Privately Held-Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation. Given the absence of a public trading market for our common stock, our board of directors exercised reasonable judgment and considered a number of objective and subjective factors to determine the best estimate of the fair value of our common stock, including (i) our business, financial condition and results of operations, including related industry trends affecting our operations; (ii) our forecasted operating performance and projected future cash flows; (iii) the illiquid nature of our common stock; (iv) the rights and privileges of our common stock; (v) market multiples of our most comparable public peers; and (vi) market conditions affecting our industry.
| 51 |
There are significant judgments and estimates inherent in these valuations. The assumptions underlying these valuations represent management’s best estimates, which involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management judgment. As a result, if factors or expected outcomes change and we use significantly different assumptions or estimates, our stock-based compensation expense could be materially different.
After the closing of the IPO, our board of directors now determine the fair value of our shares of common stock underlying stock-based awards based on the closing price of our common stock as reported by Nasdaq on the date of grant.
JOBS Act Accounting Election
The JOBS Act, permits an “emerging growth company” such as us to take advantage of an extended transition period to comply with new or revised accounting standards applicable to public companies until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Fluctuation Risk
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates. As of June 30, 2021, our cash consisted of checking and demand deposit accounts. Our primary exposure to market risk is interest income sensitivity, which is affected by changes in the general level of U.S. interest rates. Because of the short-term nature of the instruments in our portfolio and the low interest rates on our interest-bearing operating accounts, an immediate 10% change in market interest rates would not have a material impact on the fair market value of our investment portfolio or on our financial position or results of operations.
As of June 30, 2021, we had no borrowings outstanding.
Foreign Currency Fluctuation Risk
We are not currently exposed to significant market risk related to changes in foreign currency exchange rates; however, we have contracted with and may continue to contract with foreign vendors located in Europe and the United Kingdom. Our operations may be subject to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates in the future.
Inflation Fluctuation Risk
Inflation generally affects us by increasing our cost of labor and clinical trial costs. We do not believe that inflation had a material effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations for the year ended June 30, 2021.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
The financial statements required to be filed pursuant to this Item 8 are appended to this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Pursuant to Item 15, Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, see Index to the Financial Statements on page F-1 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, incorporated into this Item by reference, for a list of the financial statements included herein.
| 52 |
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and our principal financial officer, evaluated, as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act. The term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company’s management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives and management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
Based on that evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of June 30, 2021, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures as of such date are effective at the reasonable assurance level.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
This Annual Report on Form 10-K does not include a report of management’s assessment regarding internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) or an attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm due to a transition period established by rules of the SEC for newly public companies.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) during the quarter ended June 30, 2021 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this Item 10 will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2021 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
We have adopted a written code of business conduct and ethics (the “Code”), that applies to all of our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions. A current copy of the Code is available on the investor section of our website at www.anebulo.com. We intend to disclose on our website any amendments to, or waivers from, our Code that are required to be disclosed pursuant to SEC rules.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this Item 11 will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2021 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this Item 12 will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2021 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this Item 13 will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2021 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal ACCOUNTANT Fees and Services
The information required by this Item 14 will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2021 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
| 53 |
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits AND Financial Statement Schedules
Financial Statements
| PAGE | |
| Audited financial statements as of and for the year ended June 30, 2021 and as of June 30, 2020 and for the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020: | |
| Report of independent registered public accounting firm | F-2 |
| Balance sheets | F-3 |
| Statements of operations | F-4 |
| Statements of convertible preferred stock, common stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit) | F-5 |
| Statements of cash flows | F-6 |
| Notes to financial statements | F-7-17 |
Financial Statement Schedules
All financial statement schedules have been omitted, since the required information is not applicable or is not present in amounts sufficient to require submission of the schedules, or because the information required is included in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes included in this Form 10-K.
Exhibits Required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K
* Filed herewith.
† Compensatory plan or management contract.
# Certain of the schedules and attachments to this exhibit have been omitted pursuant to Regulation S-K, Item 601(a)(5). The registrant hereby undertakes to provide further information regarding such omitted materials to the Securities and Exchange Commission upon request.
Not applicable.
| 54 |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| ANEBULO PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. | ||
| Date: September 22, 2021 | By: | /s/ Daniel Schneeberger |
| Daniel Schneeberger | ||
| Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | ||
| Date: September 22, 2021 | By: | /s/ Rex Merchant |
| Rex Merchant | ||
| Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose individual signature appears below hereby authorizes and appoints Daniel Schneeberger and Rex Merchant, and each of them, with full power of substitution and re-substitution and full power to act without the other, as his or her true and lawful attorney-in-fact and agent to act in his or her name, place and stead and to execute in the name and on behalf of each person, individually and in each capacity stated below, and to file any and all amendments to this annual report on Form 10-K and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing, ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents or any of them or their or his substitute or substitutes may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue thereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Name | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Daniel Schneeberger | Chief Executive Officer and Director | September 22, 2021 | ||
| Daniel Schneeberger | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
| /s/ Joseph F. Lawler | Director and Chairman of the Board of Directors | September 22, 2021 | ||
| Joseph F. Lawler | ||||
| /s/ Rex Merchant | Chief Financial Officer | September 22, 2021 | ||
| Rex Merchant | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | |||
| /s/ Aron R. English | Director | September 22, 2021 | ||
| Aron R. English | ||||
| /s/ Jason Aryeh | Director | September 22, 2021 | ||
| Jason Aryeh | ||||
| /s/ Kenneth Lin | Director | September 22, 2021 | ||
| Kenneth Lin | ||||
| /s/ Areta Kupchyk | Director | September 22, 2021 | ||
| Areta Kupchyk | ||||
| /s/ Karah Parschauer | Director | September 22, 2021 | ||
| Karah Parschauer |
| 55 |
Index to Financial Statements
| PAGE | |
| Audited financial statements as of and for the year ended June 30, 2021 and as of June 30, 2020 and for the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020: | |
| Report of independent registered public accounting firm | F-2 |
| Balance sheets | F-3 |
| Statements of operations | F-4 |
| Statements of convertible preferred stock, common stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit) | F-5 |
| Statements of cash flows | F-6 |
| Notes to financial statements | F-7-16 |
| F-1 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (the “Company”) as of June 30, 2021 and 2020, and the related statements of operations, convertible preferred stock, common stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for the year ended June 30, 2021 and the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of June 30, 2021 and 2020 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended June 30, 2021 and the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ EisnerAmper LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2020.
EISNERAMPER LLP
Iselin, New Jersey
September 22, 2021
| F-2 |
Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 19,985,645 | $ | 3,024,980 | ||||
| Receivable - related party | - | 3,500 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 1,667,846 | - | ||||||
| Total assets | $ | 21,653,491 | $ | 3,028,480 | ||||
| Liabilities, convertible preferred stock, and stockholders’ equity (deficit) | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 110,048 | $ | - | ||||
| Accrued expenses | 131,585 | 22,579 | ||||||
| Promissory notes - related party | - | 201,286 | ||||||
| Total liabilities | 241,633 | 223,865 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||
| Series A convertible preferred stock | - | 2,975,752 | ||||||
| Stockholders’ equity (deficit): | ||||||||
| Preferred stock, $0.001 par value; 2,000,000 and no shares authorized, and no shares issued or outstanding at June 30, 2021 and 2020, respectively | - | - | ||||||
| Common stock, $0.001 par value; 40,000,000 and 22,800,000 shares authorized; 23,344,567 and 12,000,000 shares issued and outstanding at June 30, 2021 and 2020, respectively | 23,345 | 12,000 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 60,032,597 | - | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (38,644,084 | ) | (183,137 | ) | ||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) | 21,411,858 | (171,137 | ) | |||||
| Total liabilities, convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit) | $ | 21,653,491 | $ | 3,028,480 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-3 |
Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
| For the Year ended | For the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to |
|||||||
| June 30, 2021 | June 30, 2020 | |||||||
| Research and development | $ | 2,269,998 | $ | 150,000 | ||||
| General and administrative | 1,343,755 | 23,351 | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 3,613,753 | 173,351 | ||||||
| Loss from operations | (3,613,753 | ) | (173,351 | ) | ||||
| Other (income) expenses: | ||||||||
| Interest income | (1,020 | ) | - | |||||
| Interest expense | 11,767 | 1,286 | ||||||
| Fair value adjustment for Milestone Warrants | 26,626,710 | - | ||||||
| Other | 1,344 | - | ||||||
| Total other expenses, net | 26,638,801 | 1,286 | ||||||
| Net loss | $ | (30,252,554 | ) | $ | (174,637 | ) | ||
| Deemed dividends | (8,208,393 | ) | - | |||||
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (38,460,947 | ) | $ | (174,637 | ) | ||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, basic and diluted | 13,612,701 | 12,000,000 | ||||||
| Net loss per share, basic and diluted | $ | (2.83 | ) | $ | (0.01 | ) | ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-4 |
Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Statements of Convertible Preferred Stock, Common Stock and Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
For the Year Ended June 30, 2021 and the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020
| Series A | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Convertible Preferred Stock | Common Stock | Additional Paid-in | Accumulated | Stockholders’ Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Capital | Deficit | (Deficit) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at April 23, 2020 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock | - | - | 12,000,000 | 12,000 | - | (8,500 | ) | 3,500 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of Series A convertible preferred stock, net of issuance costs of $24,248 | 2,047,500 | 2,975,752 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | - | - | (174,637 | ) | (174,637 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at June 30, 2020 | 2,047,500 | $ | 2,975,752 | 12,000,000 | $ | 12,000 | $ | - | $ | 183,137 | ) | $ | (171,137 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of restricted common stock | - | - | 982,500 | 983 | (983 | ) | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Deemed dividend | - | - | - | - | - | (8,208,393 | ) | (8,208,393 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cashless exercise of Milestone Warrant into convertible preferred stock | 5,236,343 | 37,085,103 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversion of convertible preferred stock to common stock upon closing of initial public offering | (7,283,843 | ) | (40,060,855 | ) | 7,283,843 | 7,284 | 40,053,571 | - | 40,060,855 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock from initial public offering net of issuance costs of approximately $1,764,000 | - | - | 3,078,224 | 3,078 | 19,780,062 | - | 19,783,140 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | - | - | - | - | 199,947 | - | 199,947 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | - | - | (30,252,554 | ) | (30,252,554 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at June 30, 2021 | - | $ | - | 23,344,567 | $ | 23,345 | $ | 60,032,597 | $ | (38,644,084 | ) | $ | 21,411,858 | ||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-5 |
Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
| For the Year ended | For the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to |
|||||||
| June 30, 2021 | June 30, 2020 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (30,252,554 | ) | $ | (174,637 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | 199,947 | - | ||||||
| Promissory notes accrued interest | - | 1,286 | ||||||
| Fair value adjustment for Milestone Warrants | 26,626,710 | - | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| Receivable - related party | 3,500 | - | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (1,667,846 | ) | - | |||||
| Accounts payable | 110,048 | - | ||||||
| Accrued expenses | 109,006 | 22,579 | ||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (4,871,189 | ) | (150,772 | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of promissory notes to related party | - | 200,000 | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of Series A convertible preferred stock | - | 3,000,000 | ||||||
| Payment of issuance costs on Series A convertible preferred stock | - | (24,248 | ) | |||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock to the public, net of . underwriter discount | 20,604,770 | - | ||||||
| Payment of initial public offering costs | (821,630 | ) | - | |||||
| Proceeds from issuance of milestone warrants | 2,250,000 | - | ||||||
| Repayment of promissory notes, related party | (201,286 | ) | - | |||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 21,831,854 | 3,175,752 | ||||||
| Net increase in cash | 16,960,665 | 3,024,980 | ||||||
| Cash, beginning of period | 3,024,980 | - | ||||||
| Cash, end of the period | $ | 19,985,645 | $ | 3,024,980 | ||||
| Supplemental cash flow information: | ||||||||
| Cash paid for interest | $ | 13,053 | $ | - | ||||
| Supplemental Disclosure of Noncash Investing and Financing Activities: | ||||||||
| Conversion of preferred to common stock upon issuance of common stock to the public | $ | 40,060,855 | $ | - | ||||
| Proceeds due from issuance of common stock to founder | $ | - | $ | 3,500 | ||||
| Deemed dividend | $ | 8,208,393 | $ | - | ||||
| Cashless exercise of warrants into convertible preferred stock upon IPO | $ | 37,085,103 | $ | - | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-6 |
Note 1. Nature of business and basis of presentation
Organization
Anebulo Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“the Company”) was founded on April 23, 2020, as a Delaware corporation. The Company is a clinical stage biotechnology company focused on developing and commercializing new treatments for patients suffering from Acute Cannabis Intoxication (ACI) and addiction. The Company’s principal operations are located in Lakeway, Texas.
Stock Split and Initial Public Offering
On April 23, 2021, the Company effected a six-for-one stock split of its common stock to be consummated prior to the completion of the Company’s Initial Public Offering (IPO). All shares, stock options, warrants and per share information presented in the accompanying financial statements and notes thereto have been adjusted to reflect the stock split on a retroactive basis for all periods presented. There was no change in the par value of the Company’s common stock.
On May 11, 2021, the Company completed an IPO of 3,078,224 shares of its common stock, including the partial exercise by the underwriters of their option to purchase up to 450,000 additional shares of common stock, for aggregate gross proceeds of approximately $21,548,000 and its shares started trading on The Nasdaq Capital Market under the ticker symbol “ANEB.” The Company received approximately $19,783,000 in net proceeds after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and other offering expenses payable by the Company. Upon the closing of the IPO on May 11, 2021, a cashless exercise of Milestone Warrants resulted in the issuance of 5,236,343 shares of Series A convertible preferred stock and all of the outstanding shares of Series A convertible preferred stock automatically converted into 7,283,843 shares of common stock.
Liquidity and capital resources
From inception, the Company has devoted substantially all of its efforts to raising capital and acquiring licensing rights to its drug product.
Through June 30, 2021, the Company has raised approximately $5,426,000 of funding through the sales of its Series A Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series A Preferred”), Series A preferred milestone warrants, and the issuance of two promissory notes.
On May 11, 2021, the Company closed on an IPO of 3,078,224 shares of its common stock at an offering price of $7.00 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $21,548,000. Since its inception, the Company has incurred substantial losses and expects to continue to generate operating losses in the future. As of June 30, 2021, the Company had an accumulated deficit of $38,644,084 and cash of $19,985,645.
The Company believes that its existing cash will enable the Company to meet its operational liquidity needs and fund its planned investing activities for at least the next 12 months from the date of issuance of these financial statements.
Basis of presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in conformity with U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”) Any reference in these notes to applicable guidance is meant to refer to GAAP as found in the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) and Accounting Standards Updates (“ASU”) of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”).
Note 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Use of estimates
The preparation of the audited financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Among the more significant estimates included in these financial statements are those used to determine the fair value of the warrant liability, the fair value of common stock and stock-based awards, prepaid/accruals for research and development costs and uncertain tax positions. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
| F-7 |
Risk and Uncertainties
Periodically, the Company may maintain deposits in financial institutions in excess of government insured limits. Management believes that the Company is not exposed to significant credit risk as the Company’s deposits are held at financial institutions that management believes to be of high credit quality, and the Company has not experienced any losses on these deposits.
The Company operates in an industry that is subject to intense competition, government regulations and rapid technological change. Operations are subject to significant risk and uncertainties including financial, operational, technological, regulatory, and other risks, including potential risk of business failure.
In March 2020, the World Health Organization declared the global novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak a pandemic. As of June 30, 2021, the Company’s operations have not been significantly impacted by the COVID-19 outbreak. However, the Company cannot at this time predict the specific extent, duration, or full impact that the COVID-19 outbreak will have on its financial condition and operations, including ongoing and planned clinical trials.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase to be cash equivalents.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair value is applied for all financial assets and liabilities. The carrying amount of the Company’s financial instruments, including receivable-related party, accounts payable, and accrued expenses approximate fair value due to the short-term duration of those instruments. The carrying amounts of promissory notes-related party approximate fair value due to fixed interest rates approximating market interest rates.
Fair value is defined as the price received to sell an investment in a timely transaction or pay to transfer a liability in a timely transaction with an independent buyer in the principal market, or in the absence of a principal market, the most advantageous market for the investment or liability. A framework is used for measuring fair value utilizing a three-tier hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3).
The three levels of the fair value hierarchy are as follows:
Level 1—Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets that are accessible at the measurement date for identical, unrestricted assets or liabilities;
Level 2—Quoted prices in markets that are not considered to be active or financial instrument valuations for which all significant inputs are observable, either directly or indirectly; and
Level 3—Prices or valuations that require inputs that are both significant to the fair value measurement and unobservable.
Financial instruments are categorized in their entirety based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement requires judgment and considers factors specific to the investment. To the extent that the valuation is based on models or inputs that are less observable or unobservable in the market, the determination of fair value requires more judgment. Accordingly, the degree of judgment exercised by the Company in determining fair value is greatest for instruments categorized in Level 3.
| F-8 |
Convertible Preferred Stock
The Company has classified its Series A Preferred stock as temporary equity in the accompanying balance sheets due to certain change in control events that are outside of the Company’s control, including sale or transfer of control of the Company, as holders of the Series A Preferred could cause redemption of the shares in these situations. As of June 30, 2021, there was no Series A Preferred stock outstanding.
Equity Issuance Costs
The Company capitalizes incremental legal, professional, accounting and other third-party fees that are directly associated with its stock offerings as other non-current assets until the offerings are consummated. Upon consummation, these costs are recorded in stockholders’ equity (deficit) as a reduction of additional paid-in-capital generated as a result of the offerings. Should a planned equity financing be abandoned, the deferred offering costs will be expensed immediately as a charge to operating expenses in the consolidated statement of operations. After consummation of the IPO, which closed on May 11, 2021, total offering costs of approximately $822,000 were all recorded in stockholders’ equity (deficit) as a reduction of additional paid-in capital generated as a result of the offering. As of June 30, 2021, there were no deferred offering costs.
Research and Development Costs
Research and development costs are charged to expense as incurred. Payments for these activities will be based on the terms of the individual arrangements, which may differ from the pattern of costs incurred, and are reflected in the financial statements as prepaid or accrued research and development. Research and development activities may consist of salaries and benefits, contract services, materials and supplies, stock-based compensation expense, depreciation of equipment, and other outside expenses.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company recognizes stock-based compensation expense related to stock options granted to employees and non-employees based on the estimated fair value of the awards on the date of grant. The Company estimates the grant date fair value, and the resulting stock-based compensation expense, for stock options that only have service vesting requirements or performance-based vesting requirements without market conditions using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The grant date fair value of the stock-based awards with service vesting requirements is generally recognized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period of the respective awards. Determining the appropriate amount to expense for performance-based awards based on the achievement of stated goals requires judgment. The estimate of expense is revised periodically based on the probability of achieving the required performance targets and adjustments are made as appropriate. The cumulative impact of any revisions is reflected in the period of change. If any applicable financial performance goals are not met, no compensation cost is recognized, and any previously recognized compensation cost is reversed.
The Black-Scholes option-pricing model requires the use of highly subjective assumptions, which determine the fair value of stock-based awards. These assumptions include:
Expected term - Expected term represents the period that the stock-based awards are expected to be outstanding and is determined using the simplified method (based on the mid-point between the vesting date and the end of the contractual term).
Common stock price – Due to the absence of an active market for the Company’s common stock prior to the IPO, the Company utilized methodologies in accordance with the framework of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants Technical Practice Aid, Valuation of Privately-Held Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation, to estimate the fair value of its common stock. In determining the exercise prices for options granted, the Company considered the estimated fair value of the common stock as of the measurement date. The estimated fair value of the common stock has been determined at each grant date based upon a variety of factors, including the illiquid nature of the common stock, arm’s-length sales of the Company’s capital stock (including redeemable convertible preferred stock), the effect of the rights and preferences of the preferred shareholders, and the prospects of a liquidity event. Among other factors are the Company’s financial position and historical financial performance, the status of technological developments within the Company’s research, the composition and ability of the current research and management team, an evaluation or benchmark of the Company’s competition, and the current business climate in the marketplace. Significant changes to the key assumptions underlying the factors used could result in different fair values of common stock at each valuation date. Subsequent to the IPO, the Company has used the market value of its common stock on the measurement date.
| F-9 |
Expected volatility - The Company does not have any trading history prior to the IPO, or sufficient trading history subsequent for its common stock and the expected volatility was estimated using weighted-average measures of implied volatility and the historical volatility of its peer group of companies for a period equal to the expected life of the stock options. The peer group of publicly traded biopharmaceutical companies was chosen based on their similar size, stage in the life cycle or area of specialty.
Risk-free interest rate - The risk-free interest rate is based on the rates paid on securities issued by the U.S. Treasury with a term approximating the expected life of the stock options.
Expected dividend - The Company has never paid, and does not anticipate paying, cash dividends on its common stock. Therefore, the expected dividend yield was assumed to be zero.
The Company has made an entity-wide accounting policy election to account for pre-vesting award forfeitures when they occur.
Leases
The Company adopted the ASU No. 2016-02, “Leases” (“ASC 842”) effective April 23, 2020 (inception) using the modified retrospective approach. The Company has elected to apply (i) the practical expedient which allows the Company to not separate lease and non-lease components, for new leases entered into after adoption and (ii) the short-term lease exemption for all leases with an original term of less than 12 months, for purposes of applying the recognition and measurements requirements in the new standard.
The new standard establishes a right-of-use (“ROU”) model that requires a lessee to recognize a ROU asset and corresponding lease liability on the balance sheet for all leases with a term longer than 12 months. Leases will be classified as finance or operating, with classification affecting the pattern and classification of expense recognition in the income statement as well as the reduction of the right-of-use asset.
At the inception of an arrangement, the Company determines whether the arrangement is or contains a lease based on specific facts and circumstances, the existence of an identified asset(s), if any, and the Company’s control over the use of the identified asset(s), if applicable. Operating lease liabilities and their corresponding right-of-use assets are recorded based on the present value of future lease payments over the expected lease term. The interest rate implicit in lease contracts is typically not readily determinable. As such, the Company will utilize the incremental borrowing rate, which is the rate incurred to borrow on a collateralized basis over a similar term on an amount equal to the lease payments in a similar economic environment.
Operating leases are recognized on the balance sheet as ROU lease assets, lease liabilities current and lease liabilities non-current. Fixed rents are included in the calculation of the lease balances while variable costs paid for certain operating and pass-through costs are excluded. Lease expense is recognized over the expected term on a straight-line basis.
In August 2020, the Company entered into a month-to-month sub-lease for office space in Lakeway, Texas, from a related party and recorded rent expense of $12,629 and zero for the year ended June 30, 2021 and period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020, respectively.
| F-10 |
Loss Per Share
The Company’s Series A Preferred securities participate on a one-for-one basis with common stock in the distribution of dividends, if and when declared by the Board of Directors.
There were no Series A share outstanding at June 30, 2021. Since the Company has reported a net loss for the year ended June 30, 2021 and period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020, no income was allocated to the Company’s Series A Preferred securities. Basic and diluted net loss per share are the same because the impact of Series A Preferred and options would be anti-dilutive and has been excluded from the computation of diluted weighted-average shares outstanding.
Income Taxes
The Company recognizes deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the Company’s financial statements and tax returns. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based upon the differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax bases of existing assets and liabilities and for loss and credit carryforwards, using enacted tax rates expected to be in effect in the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance if it is more likely than not that these assets may not be realized. The Company determines whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination. If it is not more likely than not that a position will be sustained, none of the benefit attributable to the position is recognized. The tax benefit to be recognized for any tax position that meets the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold is calculated as the largest amount that is more than 50% likely of being realized upon resolution of the contingency. The Company accounts for interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions as part of its provision for income taxes.
Segment and geographic information
Operating segments are defined as components of an entity about which separate discrete information is available for evaluation by the chief operating decision maker, or CODM, or decision-making group, in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The CODM is the Company’s Chief Executive Officer. The Company views its operations as and manages its business in one operating segment operating exclusively in the United States. The Company has one lead product candidate, ANEB-001, under development, which was licensed from Vernalis Development Ltd in May 2020 (“License Agreement”), as described in Note 7.
Milestone Warrants
The Company accounts for Milestone Warrants as freestanding financial instruments in accordance with ASC No. 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, which requires the Company to separately account for the warrants at fair value. The fair value used for the warrants is calculated using the Black-Scholes valuation model. See Note 3.
Recently issued and adopted accounting pronouncements
The Company considers the applicability and impact of all ASUs. ASUs not discussed below were assessed and determined to be either not applicable or are expected to have minimal impact on the financial statements.
In December 2019, the FASB issued ASU No. 2019-12, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes, which simplifies the accounting for income taxes by removing certain exceptions to the general principles in the existing guidance for income taxes and making other minor improvements. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2020 with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting this new accounting guidance.
Note 3. Fair Value Measurements
The Company measured its warrant liability related to certain warrants issued to investors at fair value on a recurring basis during the year ended June 30, 2021. No financial instruments were carried at fair value during the period from April 23, 2020 (inception date) through June 30, 2020.
| F-11 |
The Company estimated the fair value of the warrant liability, determined based on Level 3 inputs, using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model upon issuance, at each balance sheet date and just prior to reclassification to equity. Changes in the fair value of the warrant liability each period were recorded in current period earnings as other expense. The Company received proceeds for the issuance of Milestone Warrants of $2,250,000 and the fair value of the warrants in excess of proceeds received of $8,208,393 was recorded as a deemed dividend, against accumulated deficit for the year ended June 30, 2021. The increase in the fair value of the warrant liability between March 8, 2021 (issuance date) and May 6, 2021 (immediately prior to exercise) was approximately $26,627,000, which was recorded in other expense for the year ended June 30, 2021. Upon IPO, the Milestone Warrants were converted via cashless exercise into Series A preferred stock and the total fair value of approximately $37,085,000 was reclassified from liability to Series A preferred stock.
| Total | ||||
| Balance at June 30, 2020 | $ | - | ||
| Fair value of warrant liability on the date of issuance | 10,458,000 | |||
| Increase in the fair value of the warrant liability between March 8, 2021 (issuance date) and May 6, 2021 | 26,627,000 | |||
| Total fair value of warrant liability prior to IPO | 37,085,000 | |||
| Warrants converted into Series A preferred stock upon cashless exercise | (37,085,000 | ) | ||
| Balance at June 30, 2021 | $ | - | ||
The assumptions used to determine the fair value of the warrant liability as of March 8, 2021 (issuance date) and termination date May 6, 2021 (immediately prior to exercise) were as follows:
| March 8, 2021 | May 6, 2021 | |||||||
| Dividend yield | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||
| Expected volatility | 49.8 | % | 49.6 | % | ||||
| Risk-free rate | 0.35 | % | 0.32 | % | ||||
| Expected term (years) | 3.0 | 2.8 | ||||||
There were no transfers between Level 1 and Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy during the year ended June 30, 2021 and the period from April 23, 2020 (inception date) through June 30, 2020.
There were no financial instruments carried at fair value on a recurring or nonrecurring basis as of June 30, 2021 and 2020.
Note 4. Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
Prepaid expenses and other current consisted of the following:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Prepaid research and development | $ | 544,435 | $ | - | ||||
| Prepaid insurance | 1,093,101 | - | ||||||
| Prepaid other | 30,310 | - | ||||||
| Total prepaid expenses | $ | 1,667,846 | $ | - | ||||
Note 5. Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses consisted of the following:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Accrued research and development | $ | 121,662 | $ | — | ||||
| Accrued legal | 9,923 | 22,579 | ||||||
| Total accrued expenses | $ | 131,585 | $ | 22,579 | ||||
| F-12 |
Note 6. Promissory Notes
On May 28, 2020 and June 18, 2020, the Company issued promissory notes (“2020 Notes”) for $175,000 and $25,000, respectively, to a related party investor. The annual interest rate on the 2020 Notes is a fixed rate of 8.0%.
On March 22, 2021, total principal of $200,000 and accrued interest of $13,053, for the promissory notes, were paid in full to the related party investor of the Company.
For the year ended June 30, 2021 and for the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2021, the Company recorded interest expense of $11,767 and $1,286, respectively.
Note 7. License Agreement
In May 2020, the Company licensed certain intellectual property, know-how and clinical trial data from Vernalis Development Limited (“Vernalis”). The initial consideration in exchange for the license was $150,000 and was recorded as research and development expense in the statement of operations for the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020. The license term shall continue unless and until terminated for cause or insolvency, sixty day written notice, or until such time as all royalties and other sums cease to be payable in accordance with the terms of the agreement. The Company is required to pay development milestone payments related to clinical trials and granting of marketing authorization ranging from $350,000 to $3,000,000, up to a total development milestone payment of $29,900,000, and sales milestone payments of $10,000,000 and $25,000,000, in the first year when cumulative annual net sales of licensed product exceeds $500,000,000 and $1,000,000,000, respectively. The Company is also required to pay single-digit royalties on product sales over the term of the contract.
As part of the IPO in May 2021, the Company issued 192,857 shares of common stock to Vernalis in lieu of future milestone payments by the Company of $1,350,000, whether or not the Company achieves those milestones. The Company recorded the $1,350,000 payment as research and development expense for year ended June 30, 2021. The Company has determined that no further milestone payments are considered probable as of June 30, 2021 and therefore no liability has been recorded.
Note 8. Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
In June 2020, the Company authorized the sale and issuance of up to 8,943,906 shares of Series A convertible preferred stock. The Series A Preferred financing was structured so that 2,047,500 shares would be issued at the first closing to one investor (“Initial Investor”) at $1.4652 per share (“First Closing”) and up to 6,896,406 shares at $1.685 per share could be issued upon the exercise of certain warrants (“Milestone Warrants”) upon achieving the following development milestones (“Development Milestones): (a) the earlier of (x) filing by the Company with the FDA of an IND, or (y) the making of an analogous regulatory filing in any foreign jurisdictions; and (b) arrangement by the Company of active pharmaceutical ingredient in amounts sufficient to facilitate the consummation of any trial to be effected pursuant to a filing.
Upon certification by the Board of Directors, the Company had the obligation to issue and the Initial Investor plus one designated additional investor (“Additional Investor”) had the right and obligation to purchase Milestone Warrants to purchase 766,266 and 6,130,140 shares of Series A Preferred, respectively and as amended. The Milestone Warrants had a purchase price of $0.32626 per share of the additional 6,896,406 shares of Series A Preferred for total proceeds of $2,250,000 and the right to purchase the additional 6,896,406 shares of Series A Preferred at $1.685 per share.
On March 8, 2021, the requisite development milestones were achieved, and therefore the Milestone Warrants were purchased for $2,250,000 in cash (See Note 3). The warrants had a three year term.
As of June 30, 2020, the Company’s convertible Series A Preferred stock consisted of the following:
| Shares authorized | 8,943,906 | |||
| Par value | $ | .0001 | ||
| Shares issued and outstanding | 2,047,500 | |||
| Carrying value | $ | 2,975,752 | ||
| Liquidation preference | $ | 3,000,000 | ||
| Common stock issuable upon conversion | 2,047,500 |
| F-13 |
Upon the closing of the IPO on May 11, 2021, a cashless exercise of Milestone Warrants resulted in the issuance of 5,236,343 shares of Series A convertible preferred stock and all of the outstanding shares of Series A convertible preferred stock automatically converted into 7,283,843 shares of common stock.
On May 4, 2021, the Company filed an amended and restated certificate of incorporation (the “Restated Certificate”) with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware in connection with the closing of its IPO. As set forth in the Restated Certificate, the Company’s authorized capital stock consists of 40,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share, and 2,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share.
In September 2020, the Company awarded 982,500 shares of restricted common stock to its Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) under the 2020 Stock Incentive Plan (“2020 Stock Incentive Plan”) at a grant date fair value of $0.11 per share. The restrictions were subject to the satisfaction of certain performance targets and vesting requirements pursuant to the award and employment agreement. The restricted common stock vested fully upon completion of the Company’s IPO in May 2021. The restricted common stock have voting and dividend rights, and therefore all 982,500 shares have been considered issued and outstanding since their date of issuance.
Note 9. Income Taxes
The reconciliation of the U.S. federal statutory rate (21%) to the Company’s effective tax rate for the year ended June 30, 2021 and for the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020 is as follows:
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| U.S. statutory federal income tax rate | 21.0 | % | 21.0 | % | ||||
| Permanent differences | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||
| Fair Value Adjustment - Warrants | -18.5 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||
| Change in valuation allowance | -2.5 | % | -21.0 | % | ||||
| Effective tax rate | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||
The significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets consist of the following at June 30, 2021 and 2020:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Net operating loss carryforwards | 497,171 | - | ||||||
| Other assets | 281,137 | |||||||
| Stock based compensation | 19,644 | 34,927 | ||||||
| Gross deferred tax assets | 797,952 | 34,927 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance | (797,952 | ) | (34,927 | ) | ||||
| Total deferred tax assets, net of valuation allowance | - | - | ||||||
The Company did not record a benefit for income taxes. ASC 740 requires a valuation allowance to reduce the deferred tax assets reported if, based on the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Based upon the level of historical U.S. losses and future projections over the period in which the net deferred tax assets are deductible, at this time, management believes it is more likely than not that the Company will not realize the benefits of these deductible differences, and as a result the Company continues to maintain a valuation allowance for the full amount of the 2021 deferred tax assets. The valuation allowance increased by $763,025 for the year ended June 30, 2021. The increase in the 2021 valuation allowance is primarily attributable to the current year loss.
| F-14 |
As of June 30, 2021, the Company had federal net operating losses of approximately $2,367,000 which are available to offset future taxable income. These net operating loss carryforwards will carryforward indefinitely but are subject to annual taxable income limitations in the year of utilization.
Under Internal Revenue Code Section 382, if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change,” the corporation’s ability to use its pre-change NOL carryforwards and other pre-change tax attributes to offset its post-change income may be limited. Generally, an ownership change occurs when certain shareholders increase their aggregated ownership by more than 50 percentage points over their lowest ownership percentage in a testing period (typically three years). The Company has not completed a study to assess whether an ownership change has occurred or whether there have been multiple ownership changes since becoming a “loss corporation” as defined in Section 382. Future changes in stock ownership, which may be outside of the Company’s control, may trigger an ownership change. In addition, future equity offerings or acquisitions that have an equity component of the purchase price could result in an ownership change. If an ownership change has occurred or does occur in the future, utilization of the NOL carryforwards or other tax attributes may be limited, which could potentially result in the expiration of a portion of the federal and state net operating losses and tax credit carryforwards before utilization, the reduction of the Company’s gross deferred tax assets and corresponding valuation allowance, and increased future tax liability to the Company.
The Company has no unrecognized tax benefits. Interest and penalty charges, if any, related to uncertain tax positions would be classified as income tax expenses in the accompanying statements of operations. At June 30, 2021 and 2020, the Company had no accrued interest or penalties related to uncertain tax positions.
Since the Company is in a loss carryforward position, the Company is generally subject to examination by the U.S. federal tax authorities for all tax years in which a loss carryforward is available. The statute of limitations for assessment by federal and state tax jurisdictions in which the Company has business operations is open for tax years ending June 30, 2020 and after.
Note 10. Stock-Based Compensation
In June 2020, the Board of Directors adopted the 2020 Stock Incentive Plan, which provided for the grant of qualified incentive stock options and nonqualified stock options or other awards to the Company’s employees, officers, directors, advisors, and outside consultants for the purchase of up to 1,650,000 shares of the Company’s common stock. Other awards include restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock appreciation rights and other stock-based awards. Other stock-based awards are awards valued in whole or in part by reference to, or are otherwise based on, shares of common stock. Stock options generally vest over a four-year period, at achievement of a performance requirement, or upon change of control (as defined in the applicable plan). The awards expire in five or ten years from the date of grant. As of June 30, 2021, the Company had 63,096 shares available for future issuance under the 2020 Stock Incentive Plan.
Stock Options
In March 2021, the Company granted non-qualified stock option awards under the 2020 Stock Incentive Plan of 604,404 shares of the Company’s common stock to its Board of Directors, an employee and consultants of the Company. These awards are subject to the satisfaction of certain performance targets and vesting requirements pursuant to the award.
The following table provides the assumptions used in determining the fair value of option awards for the year June 30, 2021:
| Expected volatility | 49.6% - 50.9% | |
| Risk-free interest rate | 0.13% - 0.64% | |
| Expected dividend yield | 0% | |
| Expected term (in years) | 2.5 – 3.6 |
| F-15 |
The following table summarizes stock option activity for the year June 30, 2021:
|
Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (Years) |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
|||||||||||||
| Outstanding at June 30, 2020 | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||
| Granted | 604,404 | $ | 2.18 | |||||||||||||
| Exercised | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||
| Forfeited | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding at June 30, 2021 | 604,404 | $ | 2.18 | 4.7 | $ | 2,802,420 | ||||||||||
| Options exercisable at June 30, 2021 | 59,664 | $ | 2.18 | 4.7 | $ | 276,642 | ||||||||||
The weighted average grant date fair value of options awarded during the year ended June 30, 2021 was approximately $0.78 per share. No stock options were granted during the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020. As of June 30, 2021, unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to unvested stock options totaled approximately $375,000, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 3.0 years.
Restricted Stock
In September 2020, the Company awarded 982,500 shares of restricted common stock to its CEO, at a grant date fair value of $0.11 per share. The restrictions are subject to the satisfaction of certain performance targets and vesting requirements pursuant to the award and employment agreement.
In the event of a change in control of our company, the CEO will be entitled to the vesting of 50% of any stock-based awards granted but not yet vested prior to the change in control event not less than six months after the change in control event, provided the CEO remains employed by our company. If the change in control event is an initial public offering, the CEO will be entitled to the full vesting of any stock-based awards. Subsequently, the Company closed its IPO in May 2021, which resulted in a change of control, and the CEO became entitled to the full vesting of his restricted common stock.
|
Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
|||||||
| Unvested as of June 30, 2020 | - | $ | - | |||||
| Issued | 982,500 | 0.11 | ||||||
| Vested | (982,500 | ) | 0.11 | |||||
| Unvested as of June 30, 2021 | - | $ | - | |||||
As of June 30, 2021, the aggregate fair value of restricted shares vested totaled $106,437.
Compensation Expense
For the year ended June 30, 2021, the Company recorded stock-based compensation expense for all restricted shares and options of $187,349 in general and administrative expenses and $12,598 in research and development expenses. No stock-based compensation expense was recognized for the period from April 23, 2020 (inception) to June 30, 2020.
Note 11. Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders
The following common stock equivalents were excluded from the calculation of net loss per share due to their anti-dilutive effect:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Series A Convertible Preferred Stock, as converted | - | 2,047,500 | ||||||
| Stock options outstanding | 604,404 | - | ||||||
| Total | 604,404 | 2,047,500 | ||||||
| F-16 |